Cardiac Dysfunction Due to Thiamine Deficiency after Hemodialysis for Biguanide-related Lactic Acidosis
- PMID: 35135918
- PMCID: PMC9593142
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8697-21
Cardiac Dysfunction Due to Thiamine Deficiency after Hemodialysis for Biguanide-related Lactic Acidosis
Abstract
Biguanide is an ideal drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. When used appropriately, the incidence of lactic acidosis is reported to be very low. Risk factors associated with biguanide-related lactic acidosis include chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, alcohol use, severe dehydration, shock, hypoxic states, sepsis, and advanced age. We herein report a case of cardiac dysfunction due to thiamine deficiency after hemodialysis in a patient with suspected biguanide-related lactic acidosis. Patients who develop severe lactic acidosis while taking biguanides should be given a large dose of thiamine without delay, given the possibility of thiamine deficiency as a complication.
Keywords: cardiac dysfunction; lactic acidosis; metformin; thiamin deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
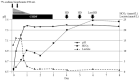
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Dramatic Recovery of a Patient with Biguanide-associated Severe Lactic Acidosis Following Thiamine Supplementation.Intern Med. 2017;56(4):455-459. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7754. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28202871 Free PMC article.
-
Biguanide-associated lactic acidosis. Case report and review of the literature.Arch Intern Med. 1992 Nov;152(11):2333-6. doi: 10.1001/archinte.152.11.2333. Arch Intern Med. 1992. PMID: 1444694 Review.
-
Lactic acidosis induced by metformin in a chronic hemodialysis patient with diabetes mellitus type 2.Hemodial Int. 2014 Apr;18(2):529-31. doi: 10.1111/hdi.12109. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Hemodial Int. 2014. PMID: 24299454
-
Biguanide related lactic acidosis: incidence and risk factors.Arch Med Res. 1992 Spring;23(1):19-24. Arch Med Res. 1992. PMID: 1308787
-
Shoshin beriberi and thiamine-responsive right heart failure: A case report in Mayotte Recognition and management of infant Shoshin beriberi.Arch Pediatr. 2022 Nov;29(8):624-625. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2022.08.017. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Arch Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36283886 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin B1 Deficiency and Perimyocarditis Fulminans: A Case Study of Shoshin Syndrome in a Woman Following an Unbalanced Dietary Pattern Followed by a Literature Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;13(1):205. doi: 10.3390/life13010205. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676154 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Role of Thiamine Supplementation in Counteracting Cardiometabolic Dysfunctions Associated with Thiamine Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3090. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073090. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey CJ, Turner RC. Metformin. N Engl J Med 334: 574-579, 1996. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo R, Fleming GA, Chen K, Bicsak TA. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: current perspectives on causes and risk. Metabolism 65: 20-29, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Misbin RI. The phantom of lactic acidosis due to metformin in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: 1791-1793, 2004. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 352: 854-865, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Cavallo-Perin P, Aluffi E, Estivi P, et al. . The hyperlactatemic effect of biguanides: a comparison between phenformin and metformin during a 6-month treatment. Riv Eur Sci Med Famacol 11: 45-49, 1989. - PubMed

