Pharmacological inhibition of Ref-1 enhances the therapeutic sensitivity of papillary thyroid carcinoma to vemurafenib
- PMID: 35136031
- PMCID: PMC8825860
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04550-0
Pharmacological inhibition of Ref-1 enhances the therapeutic sensitivity of papillary thyroid carcinoma to vemurafenib
Abstract
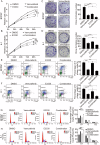
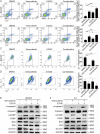
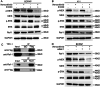
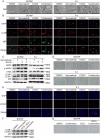
The use of the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib exhibits drug resistance in the treatment of thyroid cancer (TC), and finding more effective multitarget combination therapies may be an important solution. In the present study, we found strong correlations between Ref-1 high expression and BRAF mutation, lymph node metastasis, and TNM stage. The oxidative stress environment induced by structural activation of BRAF upregulates the expression of Ref-1, which caused intrinsic resistance of PTC to vemurafenib. Combination inhibition of the Ref-1 redox function and BRAF could enhance the antitumor effects of vemurafenib, which was achieved by blocking the action of Ref-1 on BRAF proteins. Furthermore, combination treatment could cause an overload of autophagic flux via excessive AMPK protein activation, causing cell senescence and cell death in vitro. And combined administration of Ref-1 and vemurafenib in vivo suppressed PTC cell growth and metastasis in a cell-based lung metastatic tumor model and xenogeneic subcutaneous tumor model. Collectively, our study provides evidence that Ref-1 upregulation via constitutive activation of BRAF in PTC contributes to intrinsic resistance to vemurafenib. Combined treatment with a Ref-1 redox inhibitor and a BRAF inhibitor could make PTC more sensitive to vemurafenib and enhance the antitumor effects of vemurafenib by further inhibiting the MAPK pathway and activating the excessive autophagy and related senescence process.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81702629/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82103386/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81872169/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82172821/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

