Therapeutic effects of eperisone on pulmonary fibrosis via preferential suppression of fibroblast activity
- PMID: 35136056
- PMCID: PMC8824291
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-00851-7
Therapeutic effects of eperisone on pulmonary fibrosis via preferential suppression of fibroblast activity
Abstract
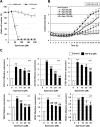
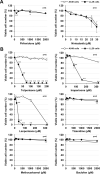
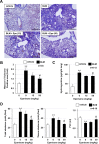
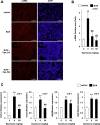
Although the exact pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is still unknown, the transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and the production of extracellular matrix components such as collagen, triggered by alveolar epithelial cell injury, are important mechanisms of IPF development. In the lungs of IPF patients, apoptosis is less likely to be induced in fibroblasts than in alveolar epithelial cells, and this process is involved in the pathogenesis of IPF. We used a library containing approved drugs to screen for drugs that preferentially reduce cell viability in LL29 cells (lung fibroblasts from an IPF patient) compared with A549 cells (human alveolar epithelial cell line). After screening, we selected eperisone, a central muscle relaxant used in clinical practice. Eperisone showed little toxicity in A549 cells and preferentially reduced the percentage of viable LL29 cells, while pirfenidone and nintedanib did not have this effect. Eperisone also significantly inhibited transforming growth factor-β1-dependent transdifferentiation of LL29 cells into myofibroblasts. In an in vivo study using ICR mice, eperisone inhibited bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis, respiratory dysfunction, and fibroblast activation. In contrast, pirfenidone and nintedanib were less effective than eperisone in inhibiting BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis under this experimental condition. Finally, we showed that eperisone did not induce adverse effects in the liver and gastrointestinal tract in the BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis model. Considering these results, we propose that eperisone may be safer and more therapeutically beneficial for IPF patients than current therapies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KT, MS, MI, TS, AT, MK, and NY do not have a financial relationship with a commercial entity that has an interest in the subject of this manuscript. TM reports receiving personal fees from LTT Bio-Pharma Co., Ltd. during the conduct of the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Idebenone has preventative and therapeutic effects on pulmonary fibrosis via preferential suppression of fibroblast activity.Cell Death Discov. 2019 Nov 18;5:146. doi: 10.1038/s41420-019-0226-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Death Discov. 2019. PMID: 31754474 Free PMC article.
-
Nintedanib solid lipid nanoparticles improve oral bioavailability and ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis in vitro and in vivo models.Int J Pharm. 2024 Jan 5;649:123644. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123644. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38040396
-
GED-0507 attenuates lung fibrosis by counteracting myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vivo and in vitro.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 16;16(9):e0257281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257281. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34529707 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Reversible Myogenic to Lipogenic Transdifferentiation Switch for the Design of Pre-clinical Drug Screening in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 15;8:569865. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.569865. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33042971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mode of action of nintedanib in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Respir J. 2015 May;45(5):1434-45. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00174914. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Eur Respir J. 2015. PMID: 25745043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time course of histopathology of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis using an intratracheal sprayer in mice.Exp Anim. 2024 Feb 14;73(1):41-49. doi: 10.1538/expanim.23-0048. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Exp Anim. 2024. PMID: 37518267 Free PMC article.
-
Ergothioneine Prevents Neuronal Cell Death Caused by the Neurotoxin 6-Hydroxydopamine.Cells. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):230. doi: 10.3390/cells13030230. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334622 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in understanding and treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent insights and emerging therapies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 7;14:1205948. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1205948. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37608885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Albumin-Fused Thioredoxin against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 5;24(11):9758. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119758. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raghu G, Rochwerg B, Zhang Y, Garcia CA, Azuma A, Behr J, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline: treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192:e3–19. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201506-1063ST. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

