Krüppel-Like Factor 6 Downregulation Is Connected with a Poor Prognosis and Tumor Growth in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35136416
- PMCID: PMC8818409
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3193553
Krüppel-Like Factor 6 Downregulation Is Connected with a Poor Prognosis and Tumor Growth in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Krüppel-Like Factor 6 Downregulation Is Connected with a Poor Prognosis and Tumor Growth in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9756782. doi: 10.1155/2023/9756782. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946991 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: Research in this article was performed to explore the biological role and clinical significance of Krüppel-like transcription factor 6 (KLF6) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
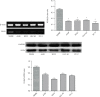
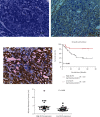
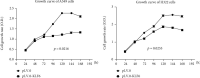
Methods: KLF6 expression in NSCLC cell lines was analyzed using reverse transcription PCR and Western blot. The expressed KLF6 protein was examined in 50 surgical NSCLC tissues using immunohistochemistry. Statistical analyses were employed for clinical association examinations. CCK8 assay and Annexin V/PI analysis were used to execute cell proliferation and apoptosis in KLF6-overexpression cell lines and the control groups. Cleaved caspase-3 expression was also detected in KLF6-overexpression cells and NSCLC tissues. KLF6 expression correlation with cleaved caspase-3 was also examined.
Results: It was discovered that downregulation of KLF6 was seen in human NSCLC cell lines. Low KLF6 expression in NSCLC tissues was correlated with poor patient prognosis (P < 0.005); patients with less KLF6 expression possessed a lower cumulative 5-year survival rate. Multivariate analysis showed KLF6 expression as an independent prognostic indicator for NSCLC individuals. Expression levels of KLF6 were associated with NSCLC tumor size (P = 0.041). Overexpression of KLF6 inhibited cell proliferation and stimulated A549 and H322 cell line apoptosis. Cleaved caspase-3 protein had higher expression levels in KLF6-overexpressed cells than in the control group. The KLF6 expression levels were positively related to the cleaved caspase-3 protein expression in NSCLC tissues (r = 0.689, P = 0.001).
Conclusions: The results indicate that downregulation of KLF6 is a significant NSCLC progression marker. KLF6 prevents cell growth and promotes cell apoptosis, possibly caspase-3 activations.
Copyright © 2022 Binbin Zeng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Krüppel-like factor 6 is frequently down-regulated and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 1;64(11):3838-43. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0185. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15172991
-
MicroRNA-100 is a potential molecular marker of non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting polo-like kinase 1.BMC Cancer. 2012 Nov 14;12:519. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-519. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23151088 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-195-5p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and a Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Directly Targeting CIAPIN1.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jul;25(3):1181-1190. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0552-z. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 30637589 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase Recruitment Domain Containing Protein 9 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Invasion via Inhibiting MAPK/p38 Pathway.Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jul;52(3):867-885. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.606. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32164050 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Krüppel-Like Transcription Factors KLF6 and KLF15 in Proximal Tubular Metabolism.Nephron. 2023;147(12):766-768. doi: 10.1159/000531336. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Nephron. 2023. PMID: 37263229 Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like factors in tumors: Key regulators and therapeutic avenues.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:1080720. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1080720. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retracted: Krüppel-Like Factor 6 Downregulation Is Connected with a Poor Prognosis and Tumor Growth in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9756782. doi: 10.1155/2023/9756782. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946991 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

