Assessment of animal diseases caused by bacteria resistant to antimicrobials: kept fish species
- PMID: 35136422
- PMCID: PMC8808658
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7076
Assessment of animal diseases caused by bacteria resistant to antimicrobials: kept fish species
Abstract
In this Opinion, the antimicrobial-resistant bacteria responsible for transmissible diseases that constitute a threat to the health of certain kept fish species have been assessed. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), carp (Cyprinus spp.), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), sea bream (Sparus aurata) and tilapia (Oreochromis spp.), selected as representative of the most important fish species and production systems that are commercially reared in fresh and saltwater farms, were the focus of this assessment. The assessment was performed following a methodology based on information collected by an extensive literature review and expert judgement. Details of the methodology used for this assessment are explained in a separate Opinion. The global state of play of antimicrobial resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas salmonicida, Flavobacterium psychrophilum and Flavobacterium columnare is provided. Among these bacteria, none was identified as being among the most relevant antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in the assessed kept fish species in the EU due to the very limited scientific evidence available.
Keywords: Animal Health Law; antimicrobial resistance; extensive literature review; fish.
© 2022 Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA on behalf of the European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
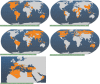
Source: FAO Cultured Aquatic Species Fact Sheets (FAO, , , , –e).

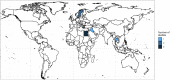

Each circle represents one study, and the size of each circle reflects how many isolates were included in the study. The colour of a circle illustrates resistance (red circle). The dashed lines indicate, for each antimicrobial, the weighted arithmetic mean of %R. The exact percentages that these lines represent are listed in Appendix C. Numbers written to the left of antimicrobial names reflect the number of studies for a certain drug/country combination.

Similar articles
-
Varying Flavobacterium psychrophilum shedding dynamics in three bacterial coldwater disease-susceptible salmonid (Family Salmonidae) species.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):e0360123. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03601-23. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38112454 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of animal diseases caused by bacteria resistant to antimicrobials: rabbits.EFSA J. 2021 Dec 23;19(12):e06999. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6999. eCollection 2021 Dec. EFSA J. 2021. PMID: 34987624 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of animal diseases caused by bacteria resistant to antimicrobials: Dogs and cats.EFSA J. 2021 Jun 28;19(6):e06680. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6680. eCollection 2021 Jun. EFSA J. 2021. PMID: 34194578 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial vaccines for fish--an update of the current situation worldwide.Dev Biol (Basel). 2005;121:55-74. Dev Biol (Basel). 2005. PMID: 15962470 Review.
-
Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013 Dec;35(6):1759-68. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.05.029. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23769873 Review.
Cited by
-
The European livestock resistome.mSystems. 2024 Apr 16;9(4):e0132823. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01328-23. Epub 2024 Mar 19. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38501800 Free PMC article.
-
Water-Mediated Dissemination and Detection of Antibiotic Resistance Across Livestock, Agri-Food, and Aquaculture Systems.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;16(8):934. doi: 10.3390/mi16080934. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baron S, Larvor E, Jouy E, Kempf I, Le Bouquin S, Chauvin C, Boitard PM, Jamin M, Le Breton A and Thuillier B, 2021. Agreement between the categorization of isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida and Yersinia ruckeri by disc diffusion and MIC tests performed at 22°C. Journal of Fish Diseases, 44, 979–985. - PubMed
-
- Beaz‐Hidalgo R, Alperi A, Buján N, Romalde JL and Figueras MJ, 2010. Comparison of phenotypical and genetic identification of Aeromonas strains isolated from diseased fish. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 33, 149–153. - PubMed
-
- CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) , 2016. Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria. CLSI guideline M45, 3rd Edition. Place Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
-
- CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) , 2020a. Methods for Antimicrobial Broth Dilution and Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated From Aquatic Animals. CLSI guideline VET03, 2nd Edition. Place Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
