The Retrievability of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer during Retreatment and the Effectiveness of Additional Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation: A Microcomputed Tomographic Study
- PMID: 35136463
- PMCID: PMC8803455
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3933305
The Retrievability of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer during Retreatment and the Effectiveness of Additional Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation: A Microcomputed Tomographic Study
Abstract
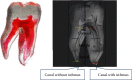
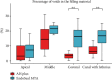
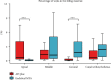
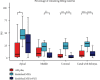
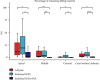
This study investigated the retreatability of EndoSeal MTA (Maruch, Wonju, Korea) according to the presence or absence of a canal isthmus and the additional use of passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) through microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) imaging. An epoxy resin sealer (AH Plus (Dentsply DeTrey, Konstanz, Germany)) was used as a reference for comparison. Forty-five artificial mandibular molars (TRUETOOTH #19, DELABS, Santa Barbara, CA) with a mesial canal with an isthmus and a distal canal without an isthmus were obturated using gutta-percha and one of the following sealers (n = 15 each): AH Plus, EndoSeal MTA, and EndoSeal MTA + PUI. Micro-CT scanning was performed to assess the void volume (as a percentage) at three root levels. After the root fillings were removed, second micro-CT scanning was conducted to evaluate the amount of remaining root filling material. The Kruskal-Wallis H test and post hoc analysis were used for between-group comparisons. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparisons between canals with and without an isthmus (p < 0.05). In the EndoSeal MTA group, the void volume and remaining filling materials were higher irrespective of the presence or absence of an isthmus. In apical lesions in the EndoSeal MTA group, the void ratio was significantly lower, and there was a significantly higher amount of remaining filling material. Regardless of the presence of an isthmus, the amount of remaining filling material of the EndoSeal + PUI group was reduced to a similar degree as the AH plus group. When performing retreatment for root canals filled with EndoSeal MTA, removal of the filling material can be more difficult in the apical region. The additional use of PUI can improve the efficacy of removal.
Copyright © 2022 TaeYeon Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of retreatability of BioRoot RCS in comparison with AH Plus.Aust Endod J. 2021 Aug;47(2):222-227. doi: 10.1111/aej.12456. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Aust Endod J. 2021. PMID: 33119208
-
Retreatability of 2 mineral trioxide aggregate-based root canal sealers: a cone-beam computed tomography analysis.J Endod. 2013 Jul;39(7):893-6. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.04.022. Epub 2013 May 14. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 23791258 Clinical Trial.
-
Retreatability of BC Sealer and AH Plus root canal sealers using new supplementary instrumentation protocol during non-surgical endodontic retreatment.Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Mar;25(3):891-899. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03376-4. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 32506324
-
Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials.Int Endod J. 2022 Mar;55 Suppl 1:119-152. doi: 10.1111/iej.13650. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Int Endod J. 2022. PMID: 34674279 Review.
-
Ultrasonic vibration and thermo-hydrodynamic technique for filling root canals: Technical overview and a case series.Int Endod J. 2021 Sep;54(9):1668-1676. doi: 10.1111/iej.13566. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Int Endod J. 2021. PMID: 33987851 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of different activation procedures on sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after endodontic retreatment via confocal laser scanning microscopy.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Sep 17;24(1):1103. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04891-6. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39289653 Free PMC article.
-
Retreatability of NeoSEALER Flo obturated with warm vertical compaction versus single-cone technique using two different retreatment systems.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Mar;27(3):286-292. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_314_23. Epub 2024 Mar 6. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38634031 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells.Int J Dent. 2023 May 31;2023:4376579. doi: 10.1155/2023/4376579. eCollection 2023. Int J Dent. 2023. PMID: 37293576 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies.Odontology. 2025 Apr 7. doi: 10.1007/s10266-025-01075-8. Online ahead of print. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 40193004 Review.
References
-
- Nair P. N., Sjögren U., Krey G., Kahnberg K. E., Sundqvist G. Intraradicular bacteria and fungi in root-filled, asymptomatic human teeth with therapy-resistant periapical lesions: a long-term light and electron microscopic follow-up study. Journal of Endodontics . 1990;16(12):580–588. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(07)80201-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin L. M., Skribner J. E., Gaengler P. Factors associated with endodontic treatment failures. Journal of Endodontics . 1992;18(12):625–627. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
