GZ17-6.02 and axitinib interact to kill renal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 35136485
- PMCID: PMC8815785
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28189
GZ17-6.02 and axitinib interact to kill renal carcinoma cells
Abstract
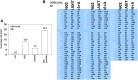
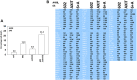
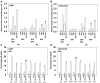
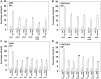
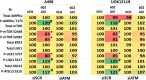
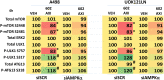
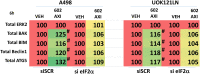
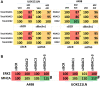
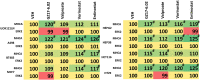
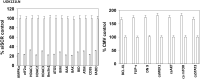
GZ17-6.02 is undergoing clinical evaluation in solid tumors and lymphoma. The present studies were performed to define its biology in renal carcinoma cells and to determine whether it interacted with axitinib to enhance tumor cell killing. GZ17-6.02 interacted in an arithmetically greater than additive fashion with axitinib to kill kidney cancer cells. GZ17-6.02 and axitinib cooperated to inactivate ERBB2, c-MET, c-KIT, c-SRC, the AMPK, STAT3, STAT5 and eIF2α and to activate PERK, ULK1 and ATG13. The drugs interacted to increase the expression of FAS-L and to decrease the levels of MCL1, BCL-XL, and HDACs 1-3. The drugs as single agents inactivated the Hippo pathway. GZ17-6.02 and axitinib interacted to enhance autophagosome formation and autophagic flux. Knock down of Beclin1, ATG5, eIF2α, toxic BH3 domain proteins or CD95/FADD significantly reduced drug combination lethality. GZ17-6.02 and axitinib increased the expression of BAK, BIM, Beclin1 and ATG5, effects blocked by knock down of eIF2α. The drugs increased phosphorylation of ULK1 S757 and ATG13 S318 and decreased the phosphorylation of mTORC1 and mTORC2, effects blocked by knock down of AMPKα. Knock down of Beclin1 or ATG5 prevented the drug combination reducing expression of HDACs 1-3 and from enhancing the expression of MHCA. Knock down of HDACs 1-3 enhanced MHCA expression. We conclude that GZ17-6.02 and axitinib interact to kill requiring ER stress signaling, autophagy and death receptor signaling. Autophagic degradation of HDACs played a key role in enhancing MHCA expression and of a potential improved response to checkpoint inhibitory immunotherapy.
Keywords: GZ17-6.02; HDAC; autophagy; axitinib; renal cell carcinoma.
Copyright: © 2022 Booth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST PD has received funding support from Genzada Pharmaceuticals Inc. for these studies. Dr. West and Dr. Moore are paid officers of the company. Dr. Dent and Dr. Von Hoff are Consultants and Key Scientific advisors to the company.
Figures
References
-
- West CE, Kwatra SG, Choi J, Von Hoff D, Booth L, Dent P. A novel plant-derived compound is synergistic with 5-fluorouracil and has increased apoptotic activity through autophagy in the treatment of actinic keratoses. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020. May 20. 10.1080/09546634.2020.1764905. . [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

