Evaluation of Low-kVp Low-Volume Iodinated Contrast Protocol for Coronary CT Angiography Using Retrospective ECG Gating
- PMID: 35136504
- PMCID: PMC8817802
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1741102
Evaluation of Low-kVp Low-Volume Iodinated Contrast Protocol for Coronary CT Angiography Using Retrospective ECG Gating
Abstract
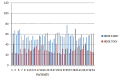
Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of low peak kilovoltage (kVp) low-volume iodinated contrast protocol for performing coronary computed tomography (CT) angiography (CCTA) in patients using retrospective electrocardiogram (ECG) gating. Materials and Methods Hundred prospective patients undergoing CCTA were studied in two groups, A and B, using 70 kilovoltage (kV) and 120 kV protocols with half and standard intravenous volumes of injected iodinated contrast, respectively. All patients had heart rates less than 100 beats/min and body mass index (BMI) less than 31 kg/m 2 . Both the groups were evaluated for signal-to-noise (S/N) and contrast-to-noise (C/N) ratios along with radiation dose delivered in millisievert (mSv), and for image quality (IQ), on per patient and per segment basis. Results Patients with group A showed statistically reduced radiation dose of 1.86 mSv compared with 6.86 mSv in group B patients. Marked reduction in image noise with statistically improved S/N and C/N ratios in all coronary vessels was seen in group A. S/N ratios in group A were 20.25, 18.68, 19.04, 17.41, and 18.69 for aorta, left main, left anterior descending, right coronary, and left circumflex arteries while they were 13.34, 11.12, 10.96, 9.74, and 8.67 in group B patients. C/N ratios were also higher in all vessels in group A patients, that is, 19.48, 19.48, 19.04, 19.48, and 17.68, compared with group B patients, who had 12.43, 10.03, 9.23, 9.57, and 8.23 ratios ( p < 0.0001). No significant difference in IQ per patient and per vessel was seen between both the groups. Discussion Retrospective ECG-gated low-kVp low-volume iodinated contrast protocol provides good diagnostic quality angiograms in patients with BMI up to 31 kg/m 2 and with heart rates of less than 100 beats/min with three times reduced radiation dose. The reduced volume of contrast reduces the cost as well as the chance of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Keywords: coronary CT angiography; low kVp; radiation.
Indian Radiological Association. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hadamitzky M et al. Radiation dose estimates from cardiac multislice computed tomography in daily practice: impact of different scanning protocols on effective dose estimates. Circulation. 2006;113(10):1305–1310. - PubMed
-
- von Ballmoos M W, Haring B, Juillerat P, Alkadhi H. Meta-analysis: diagnostic performance of low-radiation-dose coronary computed tomography angiography. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154(06):413–420. - PubMed
-
- Morsbach F, Desbiolles L, Plass A et al. Stenosis quantification in coronary CT angiography: impact of an integrated circuit detector with iterative reconstruction. Invest Radiol. 2013;48(01):32–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

