Sex Inequalities in Medical Research: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Literature
- PMID: 35136877
- PMCID: PMC8812498
- DOI: 10.1089/whr.2021.0083
Sex Inequalities in Medical Research: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Literature
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Sex Inequalities in Medical Research: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Literature by Merone et al. Womens Health Rep. 2022; 3:49-59. DOI: 10.1089/whr.2021.0083.Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2022 Mar 16;3(1):344. doi: 10.1089/whr.2021.0083.correx. eCollection 2022. Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2022. PMID: 35415710 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Historically, medical studies have excluded female participants and research data have been collected from males and generalized to females. The gender gap in medical research, alongside overarching misogyny, results in real-life disadvantages for female patients. This systematic scoping review of the literature aims to determine the extent of research into the medical research sex and gender gap and to assess the extent of misogyny, if any, in modern medical research. Methods: Initial literature searches were conducted using PubMed, Science Direct, PsychINFO and Google Scholar. Articles published between January 01, 2009, and December 31, 2019, were included. An article was deemed to display misogyny if it discussed the female aesthetic in terms of health, but did not measure health or could not be utilized to improve clinical practice. Results: Of the 17 included articles, 12 examined the gender gap in medical research and 5 demonstrated misogyny, assessing female attractiveness for alleged medical reasons. Females remain broadly under-represented in the medical literature, sex and gender are poorly reported and inadequately analyzed in research, and misogynistic perceptions continue to permeate the narrative. Conclusion: The gender gap and misogynistic studies remain present in the contemporary medical literature. Reasons and implications for practice are discussed.
Keywords: feminism; gender; gender gaps; health disparities; medicine.
© Lea Merone et al., 2022; Published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
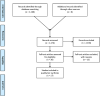
Figures
References
-
- Cheryl Carcel RN. Launch—A call to action: Sex and gender in health research: Updating policy to reflect evidence, 2019. Available at: https://www.georgeinstitute.org/news/launch-a-call-to-action-sex-and-gen... Accessed December 10, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chalmers V. Fury over scientific paper that judged women battling endometriosis on their looks 2019. Daily Mail Online. Available at: https://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-7360967/Fury-scientific-paper...
-
- Merone L. The unattractive truth about misogyny in medicine and medical research, in Croakey. Australia: Croakey Blog, 2019.
-
- McGregor AJ, Choo E. Gender-specific medicine: Yesterday's neglect, tomorrow's opportunities. Acad Emerg Med 2012;19:861–865. - PubMed
-
- Nabel EG. Coronary heart disease in women—An ounce of prevention. N Engl J Med 2000;343:572–574. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous