Sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma is a ciliopathy with somatic and bi-allelic contributions
- PMID: 35137044
- PMCID: PMC9307310
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddab366
Sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma is a ciliopathy with somatic and bi-allelic contributions
Abstract
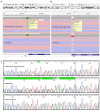
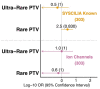
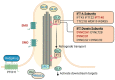
Hypothalamic hamartoma with gelastic seizures is a well-established cause of drug-resistant epilepsy in early life. The development of novel surgical techniques has permitted the genomic interrogation of hypothalamic hamartoma tissue. This has revealed causative mosaic variants within GLI3, OFD1 and other key regulators of the sonic-hedgehog pathway in a minority of cases. Sonic-hedgehog signalling proteins localize to the cellular organelle primary cilia. We therefore explored the hypothesis that cilia gene variants may underlie hitherto unsolved cases of sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma. We performed high-depth exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray on surgically resected hypothalamic hamartoma tissue and paired leukocyte-derived DNA from 27 patients. We searched for both germline and somatic variants under both dominant and bi-allelic genetic models. In hamartoma-derived DNA of seven patients we identified bi-allelic (one germline, one somatic) variants within one of four cilia genes-DYNC2I1, DYNC2H1, IFT140 or SMO. In eight patients, we identified single somatic variants in the previously established hypothalamic hamartoma disease genes GLI3 or OFD1. Overall, we established a plausible molecular cause for 15/27 (56%) patients. Here, we expand the genetic architecture beyond single variants within dominant disease genes that cause sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma to bi-allelic (one germline/one somatic) variants, implicate three novel cilia genes and reconceptualize the disorder as a ciliopathy.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations of the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Underlie Hypothalamic Hamartoma with Gelastic Epilepsy.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 4;99(2):423-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.05.031. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27453577 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-allelic SMO variants in hypothalamic hamartoma: a recessive cause of Pallister-Hall syndrome.Eur J Hum Genet. 2022 Mar;30(3):384-388. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-01023-4. Epub 2022 Jan 16. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35034092 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic variants of DYNC2H1, KIAA0556, and PTPN11 associated with hypothalamic hamartoma.Neurology. 2019 Jul 16;93(3):e237-e251. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007774. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 31197031
-
Brain mosaicism of hedgehog signalling and other cilia genes in hypothalamic hamartoma.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Sep;185:106261. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106261. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37579995 Review.
-
Surgical treatment of hypothalamic hamartoma and refractory seizures: a case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Neurosurg. 2001 Jan;34(1):40-2. doi: 10.1159/000055990. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2001. PMID: 11275785 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a presumptive sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma in a standard Schnauzer dog.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 27;12:1591863. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1591863. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40496915 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of Surgery for Hypothalamic Hamartoma-Related Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis.Neurology. 2024 Dec 24;103(12):e210060. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210060. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 39642321 Free PMC article.
-
Central precocious puberty with hypothalamic hamartoma: the first case reports of 2 siblings with different phenotypes of Seckel syndrome 5.Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Sep;28(3):225-230. doi: 10.6065/apem.2244066.033. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 35798296 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic Hamartomas: A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 5;13(2):371. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020371. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human embryonic genetic mosaicism and its effects on development and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Oct;25(10):698-714. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00715-z. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38605218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kang, S., Graham, J.M., Olney, A.H. and Biesecker, L.G. (1997) GLI3 frameshift mutations cause autosomal dominant Pallister-hall syndrome. Nat. Genet., 15, 266–268. - PubMed
-
- Johnston, J.J., Olivos-Glander, I., Killoran, C., Elson, E., Turner, J.T., Peters, K.F., Abbott, M.H., Aughton, D.J., Aylsworth, A.S., Bamshad, M.J.et al. (2005) Molecular and clinical analyses of Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly and Pallister-hall syndromes: robust phenotype prediction from the type and position of GLI3 mutations. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 76, 609–622. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saitsu, H., Sonoda, M., Higashijima, T., Shirozu, H., Masuda, H., Tohyama, J., Kato, M., Nakashima, M., Tsurusaki, Y., Mizuguchi, T.et al. (2016) Somatic mutations in GLI3 and OFD1 involved in sonic hedgehog signaling cause hypothalamic hamartoma. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol., 3, 356–365. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

