Anion-type modulates the effect of salt stress on saline lake bacteria
- PMID: 35137260
- PMCID: PMC8825391
- DOI: 10.1007/s00792-022-01260-5
Anion-type modulates the effect of salt stress on saline lake bacteria
Abstract
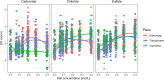
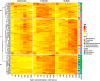
Beside sodium chloride, inland saline aquatic systems often contain other anions than chloride such as hydrogen carbonate and sulfate. Our understanding of the biological effects of salt composition diversity is limited; therefore, the aim of this study was to examine the effect of different anions on the growth of halophilic bacteria. Accordingly, the salt composition and concentration preference of 172 strains isolated from saline and soda lakes that differed in ionic composition was tested using media containing either carbonate, chloride or sulfate as anion in concentration values ranging from 0 to 0.40 mol/L. Differences in salt-type preference among bacterial strains were observed in relationship to the salt composition of the natural habitat they were isolated from indicating specific salt-type adaptation. Sodium carbonate represented the strongest selective force, while majority of strains was well-adapted to growth even at high concentrations of sodium sulfate. Salt preference was to some extent associated with taxonomy, although variations even within the same bacterial species were also identified. Our results suggest that the extent of the effect of dissolved salts in saline lakes is not limited to their concentration but the type of anion also substantially impacts the growth and survival of individual microorganisms.
Keywords: Alkaline habitat; Athalassic; Bacterioplankton; Natronophiles; Salt stress; Soda lake.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Changes in the water quality and bacterial community composition of an alkaline and saline oxbow lake used for temporary reservoir of geothermal waters.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Sep;23(17):17676-88. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6923-7. Epub 2016 May 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27240829
-
[Biodiversity of halophilic archaea isolated from two salt lakes in Xin-Jiang region of China].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006 Apr;46(2):171-6. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16736571 Chinese.
-
Limits of life in MgCl2-containing environments: chaotropicity defines the window.Environ Microbiol. 2007 Mar;9(3):801-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01212.x. Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17298378
-
Functional microbiology of soda lakes.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Jun;25:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26025021 Review.
-
Microbiology of Lonar Lake and other soda lakes.ISME J. 2013 Mar;7(3):468-76. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.137. Epub 2012 Nov 22. ISME J. 2013. PMID: 23178675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Analyses of a Rhodobium marinum RH-AZ Genome and Its Application for Promoting the Growth of Rice Under Saline Stress.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;14(16):2516. doi: 10.3390/plants14162516. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872139 Free PMC article.
-
Salinity and Heavy Metal Tolerance, and Phytoextraction Potential of Ranunculus sceleratus Plants from a Sandy Coastal Beach.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;12(12):1959. doi: 10.3390/life12121959. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexe M, Serban G, Baricz A, Andrei AS, Cristea A, Battes KP, Cîmpean M, Momeu L, Muntean V, Porab SA, Banciu HL. Limnology and plankton diversity of salt lakes from Transylvanian Basin (Romania): A review. J Limnol. 2017;77:17–34. doi: 10.4081/jlimnol.2017.1657. - DOI
-
- Banciu H, Sorokin DY, Muyzer G, Kleerebezem R, Galinski EA, Kuenen JG. Thioalkalivibrio halophilus sp. nov, a novel obligately chemolithoautotrophic facultatively alkaliphilic and extremely salt-tolerant sulfur-oxidizing bacterium from a hypersaline alkaline lake. Extremophiles. 2004;8:325–334. doi: 10.1007/s00792-004-0391-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

