Ferroptosis‑related long non‑coding RNAs and the roles of LASTR in stomach adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35137922
- PMCID: PMC8855154
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12634
Ferroptosis‑related long non‑coding RNAs and the roles of LASTR in stomach adenocarcinoma
Abstract
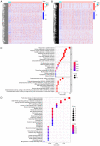
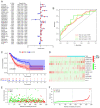
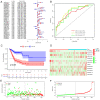
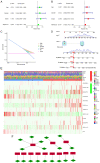
Ferroptosis is a form of programmed cell death that participates in diverse physiological processes. Increasing evidence suggests that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate ferroptosis in tumors, including stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD). In the present study, RNA‑sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database and ferroptosis‑related markers from the FerrDb data resource were analyzed to select differentially expressed lncRNAs. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed on these differentially expressed lncRNAs to screen 12 lncRNAs linked with overall survival (OS) and 13 associated with progression‑free survival (PFS). Subsequently, two signatures for predicting OS and PFS were established based on these lncRNAs. Kaplan‑Meier analyses indicated that the high‑risk group of patients with STAD had relatively poor prognosis. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves of the two signatures indicated their excellent efficacy in predicting STAD prognosis. In addition, the effect of the lncRNA LASTR on proliferation and migration in gastric cancer was confirmed and the relationship between LASTR and ferroptosis was initially explored through experiments. These results provide potential novel targets for tumor treatment and promote personalized medicine.
Keywords: LASTR; TCGA; ferroptosis; lncRNA; prognosis signature; stomach adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

