Intrathecal Synthesis Index of Specific Anti- Treponema IgG: a New Tool for the Diagnosis of Neurosyphilis
- PMID: 35138118
- PMCID: PMC8826818
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01477-21
Intrathecal Synthesis Index of Specific Anti- Treponema IgG: a New Tool for the Diagnosis of Neurosyphilis
Abstract
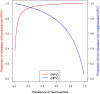
Neurosyphilis (NS) diagnosis is challenging because clinical signs are diverse and unspecific, and a sensitive and specific laboratory test is lacking. We tested the performance of an antibody index (AI) for intrathecal synthesis of specific anti-Treponema IgG by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for NS diagnosis. We conducted a retroprospective monocentric study including adults with neurological symptoms who had serum and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) samples collected between 2006 and 2021. Two NS definitions were used. NS1 included patients with neurological symptoms, positive Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA) serology, and CSF-TPPA of ≥320, as well as CSF-leukocytes of >5 cells/mm3 and/or CSF-protein of >0.45 g/L and/or a reactive CSF-VDRL/RPR test. NS2 included patients with acute ocular and/or otologic symptoms, positive TPPA serology, and a response to NS treatment. Controls were patients with central nervous system disorders other than neurosyphilis. Anti-Treponema pallidum IgG were measured simultaneously in serum and CSF, and AI was calculated according to Reiber diagram. We assessed the AI test area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity/specificity, and estimated positive and negative predictive values. In total, 16 NS1 patients, 11 NS2 patients, and 71 controls were included. With an AI of ≥1.7 as a positive test for NS diagnostic, specificity was 98.6% (95% confidence interval [CI 95%] of 92.4 to 100.0) and sensitivity was 81.3% (CI 95% of 54.4 to 96.0) for NS1 and 98.6% (CI 95% 92.4 to 100.0) and 27.3% (CI 95% 6.0 to 61.0), respectively, for NS2. Positive and negative predictive values were >95% for NS1 and >85% for NS2, for prevalence above and below 20%. Measuring an AI for intrathecal synthesis of specific anti-Treponema pallidum IgG is a new promising tool highly specific for NS diagnosis. IMPORTANCE In the context of a lack of a gold standard for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis due to either nonspecific or nonsensitive tests, we present in this article a new promising tool highly specific for NS diagnosis. This new test involves measuring an intrathecal synthesis index of specific anti-Treponema IgG by ELISA.
Keywords: intrathecal synthesis; neurosyphilis; ocular syphilis; otosyphilis; specific anti-treponema IgG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multicentric evaluation of a specific intrathecal anti-Treponema pallidum IgG index as a diagnostic biomarker of neurosyphilis: results from a retro-prospective case-control study.Sex Transm Infect. 2024 Feb 19;100(2):63-69. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2023-055913. Sex Transm Infect. 2024. PMID: 38071543
-
Comparison of intrathecal synthesis of Treponema pallidum-specific IgG antibodies and polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis.Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1996 Mar;283(3):295-305. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(96)80063-6. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1996. PMID: 8861867
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay for Neurosyphilis Diagnosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Jun;55(6):1865-1870. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00310-17. Epub 2017 Apr 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28381602 Free PMC article.
-
Syphilis: test procedures and therapeutic strategies.Semin Dermatol. 1990 Jun;9(2):152-9. Semin Dermatol. 1990. PMID: 2202411 Review.
-
The Diagnostic Performance of Laboratory Tests of Neurosyphilis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Eur Neurol. 2023;86(6):418-429. doi: 10.1159/000531341. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Eur Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37549649
Cited by
-
Neurosyphilis: insights into its pathogenesis, susceptibility, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1340321. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1340321. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38274871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Neurosyphilis: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, immunology and treatment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 19;10:1191113. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1191113. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37153093 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chronic meningitis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 1;38(3):252-260. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000001107. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40183580 Review.
-
Intrathecal immunoglobin synthesis and its role in patients with neurosyphilis.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 7;10:1008595. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1008595. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36419997 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Interleukin-26 is a Potential Biomarker for the Differential Diagnosis of Neurosyphilis and Syphilis at Other Stages.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Jul 14;15:3693-3702. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S366308. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35859909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, New York City STD Prevention Training Center. 2019. The diagnosis, management and prevention of syphilis: an update and review. https://www.ncsddc.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Syphilis_Monograph_201....
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 2019. Syphilis and congenital syphilis in Europe: a review of epidemiological trends (2007–2018) and options for response. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/syphilis-and-congenital-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous