The Interferon-Inducible Human PLSCR1 Protein Is a Restriction Factor of Human Cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 35138119
- PMCID: PMC8826943
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01342-21
The Interferon-Inducible Human PLSCR1 Protein Is a Restriction Factor of Human Cytomegalovirus
Abstract
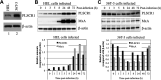
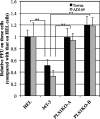
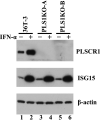
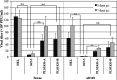
Human phospholipid scramblase 1 (PLSCR1) is strongly expressed in response to interferon (IFN) treatment and viral infection, and it has been suggested to play an important role in IFN-dependent antiviral responses. In this study, we showed that the levels of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) plaque formation in OUMS-36T-3 (36T-3) cells with high basal expression of PLSCR1 were significantly lower than those in human embryonic lung (HEL) cells with low basal expression of PLSCR1. In addition, the levels of HCMV plaque formation and replication in PLSCR1-knockout (KO) 36T-3 cells were significantly higher than those in parental 36T-3 cells and were comparable to those in HEL cells. Furthermore, compared to that in PLSCR1-KO cells, the expression of HCMV major immediate early (MIE) proteins was repressed and/or delayed in parental 36T-3 cells after HCMV infection. We also showed that PLSCR1 expression decreased the levels of the cAMP-responsive element (CRE)-binding protein (CREB)•HCMV immediate early protein 2 (IE2) and CREB-binding protein (CBP)•IE2 complexes, which have been suggested to play important roles in the IE2-mediated transactivation of the viral early promoter through interactions with CREB, CBP, and IE2. Interestingly, PLSCR1 expression repressed CRE- and HCMV MIE promoter-regulated reporter gene activities. These observations reveal, for the first time, that PLSCR1 negatively regulates HCMV replication by repressing the transcription from viral MIE and early promoters, and that PLSCR1 expression may contribute to the IFN-mediated suppression of HCMV infection. IMPORTANCE Because several IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) have been reported to suppress HCMV replication, HCMV replication is thought to be regulated by an IFN-mediated host defense mechanism, but the mechanism remains unclear. PLSCR1 expression is induced in response to viral infection and IFN treatment, and PLSCR1 has been reported to play an important role in IFN-dependent antiviral responses. Here, we demonstrate that HCMV plaque formation and major immediate early (MIE) gene expression are significantly increased in PLSCR1-KO human fibroblast cells. PLSCR1 reduces levels of the CREB•IE2 and CBP•IE2 complexes, which have been suggested to play important roles in HCMV replication through its interactions with CREB, CBP, and IE2. In addition, PLSCR1 expression represses transcription from the HCMV MIE promoter. Our results indicate that PLSCR1 plays important roles in the suppression of HCMV replication in the IFN-mediated host defense system.
Keywords: genome editing; human cytomegalovirus; interferon-stimulated genes; phospholipid scramblase 1; protein-protein interactions; restriction factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

