TNF-α Levels in Respiratory Samples Are Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 35138148
- PMCID: PMC8826736
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01411-21
TNF-α Levels in Respiratory Samples Are Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Keywords: IL-6; SARS-CoV-2; cytokines; tumor necrosis factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
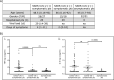
Figures
References
-
- Del Valle DM, Kim-Schulze S, Huang HH, Beckmann ND, Nirenberg S, Wang B, Lavin Y, Swartz TH, Madduri D, Stock A, Marron TU, Xie H, Patel M, Tuballes K, Van Oekelen O, Rahman A, Kovatch P, Aberg JA, Schadt E, Jagannath S, Mazumdar M, Charney AW, Firpo-Betancourt A, Mendu DR, Jhang J, Reich D, Sigel K, Cordon-Cardo C, Feldmann M, Parekh S, Merad M, Gnjatic S. 2020. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat Med 26:1636–1643. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

