A biological nanofoam: The wall of coniferous bisaccate pollen
- PMID: 35138906
- PMCID: PMC8827650
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd0892
A biological nanofoam: The wall of coniferous bisaccate pollen
Abstract
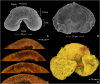
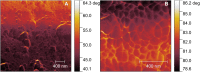
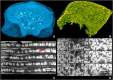
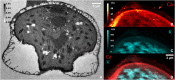
The outer layer of the pollen grain, the exine, plays a key role in the survival of terrestrial plant life. However, the exine structure in different groups of plants remains enigmatic. Here, modern and fossil coniferous bisaccate pollen were examined to investigate the detailed three-dimensional structure and properties of the pollen wall. X-ray nanotomography and volume electron microscopy are used to provide high-resolution imagery, revealing a solid nanofoam structure. Atomic force microscopy measurements were used to compare the pollen wall with other natural and synthetic foams and to demonstrate that the mechanical properties of the wall in this type of pollen are retained for millions of years in fossil specimens. The microscopic structure of this robust biological material has potential applications in materials sciences and also contributes to our understanding of the evolutionary success of conifers and other plants over geological time.
Figures

References
-
- C. H. Wellman, The Evolution of Plant Physiology (Elsevier, 2004), pp. 43–63.
-
- Watson J. S., Sephton M. A., Sephton S. V., Self S., Fraser W. T., Lomax B. H., Gilmour I., Wellman C. H., Beerling D. J., Rapid determination of spore chemistry using thermochemolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 6, 689–694 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Jardine P. E., Abernethy F. A. J., Lomax B. H., Gosling W. D., Fraser W. T., Shedding light on sporopollenin chemistry, with reference to UV reconstructions. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 238, 1–6 (2017).
-
- Li F.-S., Phyo P., Jacobowitz J., Hong M., Weng J.-K., The molecular structure of plant sporopollenin. Nat. Plants 5, 41–46 (2019). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

