Phase II Study of Taselisib in PIK3CA-Mutated Solid Tumors Other Than Breast and Squamous Lung Cancer: Results From the NCI-MATCH ECOG-ACRIN Trial (EAY131) Subprotocol I
- PMID: 35138919
- PMCID: PMC8865530
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.21.00424
Phase II Study of Taselisib in PIK3CA-Mutated Solid Tumors Other Than Breast and Squamous Lung Cancer: Results From the NCI-MATCH ECOG-ACRIN Trial (EAY131) Subprotocol I
Erratum in
-
Erratum.JCO Precis Oncol. 2022 Mar;6:e2200116. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00116. JCO Precis Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35294227 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: PIK3CA mutations frequently contribute to oncogenesis in solid tumors. Taselisib, a potent and selective inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, has demonstrated clinical activity in PIK3CA-mutant breast cancer. Whether PIK3CA mutations predict sensitivity to taselisib in other cancer types is unknown. National Cancer Institute-Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice Arm EAY131-I is a single-arm, phase II study of the safety and efficacy of taselisib in patients with advanced cancers.
Methods: Eligible patients had tumors with an activating PIK3CA mutation. Patients with breast or squamous cell lung carcinoma, or whose cancer had KRAS or PTEN mutations, were excluded. Patients received taselisib 4 mg, orally once daily continuously, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was objective response rate. Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS), 6-month PFS, overall survival (OS), and identification of predictive biomarkers.
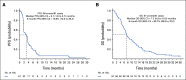
Results: Seventy patients were enrolled, and 61 were eligible and initiated protocol therapy. Types of PIK3CA mutations included helical 41 of 61 (67%), kinase 11 of 61 (18%), and other 9 of 61 (15%). With a median follow-up of 35.7 months, there were no complete or partial responses. Six-month PFS was 19.9% (90% CI, 12.0 to 29.3) and median PFS was 3.1 months (90% CI, 1.8 to 3.7). Six-month OS was 60.7% (90% CI, 49.6 to 70.0) and median OS was 7.2 months (90% CI, 5.9 to 10.0). Individual comutations were too heterogeneous to correlate with clinical outcome. Fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, and hyperglycemia were the most common toxicities, and most were grade 1 and 2.
Conclusion: In this study, taselisib monotherapy had very limited activity in a heterogeneous cohort of heavily pretreated cancer patients with PIK3CA-mutated tumors; the presence of a PIK3CA mutation alone does not appear to be a sufficient predictor of taselisib activity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02465060.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Cantley LC.The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway Science 2961655–16572002 - PubMed
-
- Guertin DA, Sabatini DM.Defining the role of mTOR in cancer Cancer Cell 129–222007 - PubMed
-
- Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, et al. The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers Cancer Biol Ther 3772–7752004 - PubMed
-
- Massion PP, Taflan PM, Shyr Y, et al. Early involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in lung cancer progression Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1701088–10942004 - PubMed
-
- Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, et al. PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer Nat Genet 2199–1021999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189953/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233329/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

