Safety and efficacy of mass drug administration with a single-dose triple-drug regimen of albendazole + diethylcarbamazine + ivermectin for lymphatic filariasis in Papua New Guinea: An open-label, cluster-randomised trial
- PMID: 35139070
- PMCID: PMC8863226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010096
Safety and efficacy of mass drug administration with a single-dose triple-drug regimen of albendazole + diethylcarbamazine + ivermectin for lymphatic filariasis in Papua New Guinea: An open-label, cluster-randomised trial
Abstract
Background: Papua New Guinea (PNG) has a high burden of lymphatic filariasis (LF) caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, with an estimated 4.2 million people at risk of infection. A single co-administered dose of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and albendazole (IDA) has been shown to have superior efficacy in sustained clearance of microfilariae compared to diethylcarbamazine and albendazole (DA) in small clinical trials. A community-based cluster-randomised trial of DA versus IDA was conducted to compare the safety and efficacy of IDA and DA for LF in a moderately endemic, treatment-naive area in PNG.
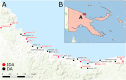
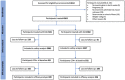
Methodology: All consenting, eligible residents of 24 villages in Bogia district, Madang Province, PNG were enrolled, screened for W. bancrofti antigenemia and microfilaria (Mf) and randomised to receive IDA (N = 2382) or DA (N = 2181) according to their village of residence. Adverse events (AE) were assessed by active follow-up for 2 days and passive follow-up for an additional 5 days. Antigen-positive participants were re-tested one year after MDA to assess treatment efficacy.
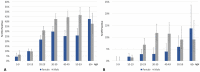
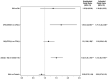
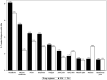
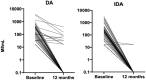
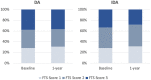
Principal findings: Of the 4,563 participants enrolled, 96% were assessed for AEs within 2 days after treatment. The overall frequency of AEs were similar after either DA (18%) or IDA (20%) treatment. For those individuals with AEs, 87% were mild (Grade 1), 13% were moderate (Grade 2) and there were no Grade 3, Grade 4, or serious AEs (SAEs). The frequency of AEs was greater in Mf-positive than Mf-negative individuals receiving IDA (39% vs 20% p<0.001) and in Mf-positive participants treated with IDA (39%), compared to those treated with DA (24%, p = 0.023). One year after treatment, 64% (645/1013) of participants who were antigen-positive at baseline were re-screened and 74% of these participants (475/645) remained antigen positive. Clearance of Mf was achieved in 96% (52/54) of infected individuals in the IDA arm versus 84% (56/67) of infected individuals in the DA arm (relative risk (RR) 1.15; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.30; p = 0.019). Participants receiving DA treatment had a 4-fold higher likelihood of failing to clear Mf (RR 4.67 (95% CI: 1.05 to 20.67; p = 0.043). In the DA arm, a significant predictor of failure to clear was baseline Mf density (RR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.09 to 2.88; p = 0.007).
Conclusion: IDA was well tolerated and more effective than DA for clearing Mf. Widespread use of this regimen could accelerate LF elimination in PNG.
Trial registration: Registration number NCT02899936; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02899936.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Author Steven Kumai was unable to confirm their authorship contributions. On their behalf, the corresponding author has reported their contributions to the best of their knowledge.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An open label, block randomized, community study of the safety and efficacy of co-administered ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine plus albendazole vs. diethylcarbamazine plus albendazole for lymphatic filariasis in India.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Feb 16;15(2):e0009069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009069. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33591979 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of co-administered diethylcarbamazine, albendazole and ivermectin during mass drug administration for lymphatic filariasis in Haiti: Results from a two-armed, open-label, cluster-randomized, community study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Jun 8;14(6):e0008298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008298. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32511226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of a single co-administered dose of diethylcarbamazine, albendazole and ivermectin in adults with and without Wuchereria bancrofti infection in Côte d'Ivoire.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 May 20;13(5):e0007325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007325. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31107869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Model-based analysis of trial data: microfilaria and worm-productivity loss after diethylcarbamazine-albendazole or ivermectin-albendazole combination therapy against Wuchereria bancrofti.Trop Med Int Health. 2006 May;11(5):718-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01606.x. Trop Med Int Health. 2006. PMID: 16640625 Review.
-
Albendazole alone or in combination with microfilaricidal drugs for lymphatic filariasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 8;1(1):CD003753. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003753.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30620051 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Managing host-parasite interactions in humans and wildlife in times of global change.Parasitol Res. 2022 Nov;121(11):3063-3071. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07649-7. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 36066742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and tolerability of moxidectin and ivermectin combination treatments for lymphatic filariasis in Côte d'Ivoire: A randomized controlled superiority study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Sep 18;17(9):e0011633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011633. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37721964 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factors associated with never treatment and acceptability of mass drug administration for the elimination of lymphatic filariasis in Guyana, 2021.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Apr 25;4(4):e0001985. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001985. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38662738 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerating Progress Towards the 2030 Neglected Tropical Diseases Targets: How Can Quantitative Modeling Support Programmatic Decisions?Clin Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 25;78(Suppl 2):S83-S92. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae082. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38662692 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Microfilaremic Individuals after Mass Drug Treatment with Ivermectin, Diethylcarbamazine, and Albendazole for Lymphatic Filariasis in Papua New Guinea.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025 Mar 25;112(6):1235-1239. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.24-0382. Print 2025 Jun 4. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025. PMID: 40132219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis: progress report, 2019. Weekly epidemiological record. 2020;No 43(95):509–24.
-
- Lenk EJ, Redekop WK, Luyendijk M, Rijnsburger AJ, Severens JL. Productivity Loss Related to Neglected Tropical Diseases Eligible for Preventive Chemotherapy: A Systematic Literature Review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(2):e0004397. Epub 2016/02/20. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004397 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Lymphatic filariasis: Progress report 2000–2009 and strategic plan 2010–2020. WHO Global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (GPELF); WHO/HTM/NTD/PCT/20106 2010.
-
- WHO. Global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis: progress report, 2018. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

