Hydroxychloroquine for prophylaxis of COVID-19 in health workers: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 35139097
- PMCID: PMC8827445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261980
Hydroxychloroquine for prophylaxis of COVID-19 in health workers: A randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Health care workers are at high risk of being infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Our aim is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) for prophylaxis of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) in health personnel exposed to patients infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Methods: Double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled single center clinical trial. Included subjects were health care workers caring for severe COVID-19 patients. Main outcome was time to symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
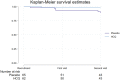
Results: 127 subjects with a confirmed baseline negative RT-PCR SARS-CoV2 test were included in the trial. 62 assigned to HCQ and 65 to placebo. One subject (1.6%) in the HCQ group and 6 (9.2%) subjects in the placebo group developed COVID-19 (Log-Rank test p = 0.07). No severe COVID-19 cases were observed. The study was suspended because of a refusal to participate and losses to follow up after several trials reported lack of effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Conclusion: The effect size of hydroxychloroquine was higher than placebo for COVID-19 symptomatic infection in health personnel, although this was not statistically significant. The trial is underpowered due to the failure to complete the estimated sample size.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Controlled, double-blind, randomized trial to assess the efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine chemoprophylaxis in SARS CoV2 infection in healthcare personnel in the hospital setting: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04400-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493494 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-exposure prophylaxis with hydroxychloroquine for high-risk healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A structured summary of a study protocol for a multicentre, double-blind randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jul 29;21(1):688. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04621-7. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32727613 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of hydroxychloroquine for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among adults exposed to coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04446-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493478 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic - A Narrative Review of the Potential Roles of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine.Pain Physician. 2020 Aug;23(4S):S351-S366. Pain Physician. 2020. PMID: 32942793 Review.
-
Effect of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine on COVID-19 virological outcomes: An updated meta-analysis.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jul-Dec;38(3 & 4):265-272. doi: 10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_20_330. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33154234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for the prevention of COVID-19 (COPCOV): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2024 Sep 12;21(9):e1004428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004428. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Med. 2024. PMID: 39264960 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety of Hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 Prophylaxis in Healthcare Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Feb 25;17(2):e79660. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79660. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40161134 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials of hydroxychloroquine for the prevention of COVID-19.Eur J Epidemiol. 2022 Aug;37(8):789-796. doi: 10.1007/s10654-022-00891-4. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Eur J Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35943669 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Activation of PARP as a SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Target-Is It a Bait for the Virus or the Best Deal We Could Ever Make with the Virus? Is AMBICA the Potential Cure?Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 16;13(2):374. doi: 10.3390/biom13020374. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxychloroquine for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 in health care workers: a randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial Healthcare Worker Exposure Response and Outcomes of Hydroxychloroquine (HERO-HCQ).Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Apr;129:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.019. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36682681 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Colaneri M, Novelli V, Cutti S, et al. The experience of the health care workers of a severely hit SARS-CoV-2 referral Hospital in Italy: incidence, clinical course and modifiable risk factors for COVID-19 infection. J Public Health (Bangkok). Published online 2020:1–9. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdaa195 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 has infected some 570,000 health workers and killed 2,500 in the Americas, PAHO Director says—PAHO/WHO | Pan American Health Organization. Accessed March 7, 2021. https://www.paho.org/en/news/2-9-2020-covid-19-has-infected-some-570000-...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous