Structure, Immunogenicity, and IgE Cross-Reactivity among Walnut and Peanut Vicilin-Buried Peptides
- PMID: 35139305
- PMCID: PMC8959100
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07225
Structure, Immunogenicity, and IgE Cross-Reactivity among Walnut and Peanut Vicilin-Buried Peptides
Abstract
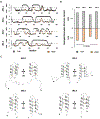
Vicilin-buried peptides (VBPs) from edible plants are derived from the N-terminal leader sequences (LSs) of seed storage proteins. VBPs are defined by a common α-hairpin fold mediated by conserved CxxxCx(10-14)CxxxC motifs. Here, peanut and walnut VBPs were characterized as potential mediators of both peanut/walnut allergenicity and cross-reactivity despite their low (∼17%) sequence identity. The structures of one peanut (AH1.1) and 3 walnut (JR2.1, JR2.2, JR2.3) VBPs were solved using solution NMR, revealing similar α-hairpin structures stabilized by disulfide bonds with high levels of surface similarity. Peptide microarrays identified several peptide sequences primarily on AH1.1 and JR2.1, which were recognized by peanut-, walnut-, and dual-allergic patient IgE, establishing these peanut and walnut VBPs as potential mediators of allergenicity and cross-reactivity. JR2.2 and JR2.3 displayed extreme resilience against endosomal digestion, potentially hindering epitope generation and likely contributing to their reduced allergic potential.
Keywords: IgE epitopes; cross-reactivity; vicilin-buried peptide; α-hairpinin.
Figures



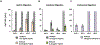
References
-
- Burney P; Summers C; Chinn S; Hooper R; Van Ree R; Lidholm J Prevalence and Distribution of Sensitization to Foods in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey: A EuroPrevall Analysis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 2010, 65 (9), 1182–1188. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02346.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

