Suppression of premature transcription termination leads to reduced mRNA isoform diversity and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 35139363
- PMCID: PMC9035109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.018
Suppression of premature transcription termination leads to reduced mRNA isoform diversity and neurodegeneration
Abstract
Tight regulation of mRNA isoform expression is essential for neuronal development, maintenance, and function; however, the repertoire of proteins that govern isoform composition and abundance remains incomplete. Here, we show that the RNA kinase CLP1 regulates mRNA isoform expression through suppression of proximal cleavage and polyadenylation. We found that human stem-cell-derived motor neurons without CLP1 or with the disease-associated CLP1 p.R140H variant had distinct patterns of RNA-polymerase-II-associated cleavage and polyadenylation complex proteins that correlated with polyadenylation site usage. These changes resulted in imbalanced mRNA isoform expression of long genes important for neuronal function that were recapitulated in vivo. Strikingly, we observed the same pattern of reduced mRNA isoform diversity in 3' end sequencing data from brain tissues of patients with neurodegenerative disease. Together, our results identify a previously uncharacterized role for CLP1 in mRNA 3' end formation and reveal an mRNA misprocessing signature in neurodegeneration that may suggest a common mechanism of disease.
Keywords: CLP1; alternative polyadenylation; co-transcriptional mRNA processing; motor neuron disease; pontocerebellar hypoplasia.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


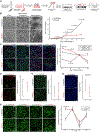

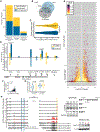
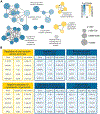
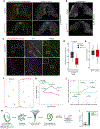

Comment in
-
CLP1-dependent premature transcription termination opposes neurodegeneration.Neuron. 2022 Apr 20;110(8):1277-1280. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.03.012. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35447096
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 CA223893/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125086/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS123524/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS077888/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HD082337/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS121374/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM144114/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS114510/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 NS116119/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS122207/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 NS085037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

