Targeted proteomics improves cardiovascular risk prediction in secondary prevention
- PMID: 35139537
- PMCID: PMC9020984
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac055
Targeted proteomics improves cardiovascular risk prediction in secondary prevention
Abstract
Aims: Current risk scores do not accurately identify patients at highest risk of recurrent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) in need of more intensive therapeutic interventions. Advances in high-throughput plasma proteomics, analysed with machine learning techniques, may offer new opportunities to further improve risk stratification in these patients.
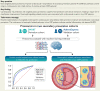
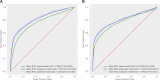
Methods and results: Targeted plasma proteomics was performed in two secondary prevention cohorts: the Second Manifestations of ARTerial disease (SMART) cohort (n = 870) and the Athero-Express cohort (n = 700). The primary outcome was recurrent ASCVD (acute myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke, and cardiovascular death). Machine learning techniques with extreme gradient boosting were used to construct a protein model in the derivation cohort (SMART), which was validated in the Athero-Express cohort and compared with a clinical risk model. Pathway analysis was performed to identify specific pathways in high and low C-reactive protein (CRP) patient subsets. The protein model outperformed the clinical model in both the derivation cohort [area under the curve (AUC): 0.810 vs. 0.750; P < 0.001] and validation cohort (AUC: 0.801 vs. 0.765; P < 0.001), provided significant net reclassification improvement (0.173 in validation cohort) and was well calibrated. In contrast to a clear interleukin-6 signal in high CRP patients, neutrophil-signalling-related proteins were associated with recurrent ASCVD in low CRP patients.
Conclusion: A proteome-based risk model is superior to a clinical risk model in predicting recurrent ASCVD events. Neutrophil-related pathways were found in low CRP patients, implying the presence of a residual inflammatory risk beyond traditional NLRP3 pathways. The observed net reclassification improvement illustrates the potential of proteomics when incorporated in a tailored therapeutic approach in secondary prevention patients.
Keywords: ASCVD; C-reactive protein; Machine learning; NLRP3; Proteomics; Risk score.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Proteomics for the prediction and prevention of atherosclerotic disease.Eur Heart J. 2022 Apr 19;43(16):1578-1581. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac036. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35165698 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jernberg T, Hasvold P, Henriksson M, Hjelm H, Thuresson M, Janzon M. Cardiovascular risk in post-myocardial infarction patients: nationwide real world data demonstrate the importance of a long-term perspective. Eur Heart J 2015;36:1163–1170. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, Honarpour N, Wiviott SD, Murphy SA, et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1713–1722. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Steg PG, Szarek M, Bhatt DL, Bittner VA, Diaz R, et al. Alirocumab and cardiovascular outcomes after acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2097–2107. - PubMed
-
- Eikelboom JW, Connolly SJ, Bosch J, Dagenais GR, Hart RG, Shestakovska O, et al. Rivaroxaban with or without aspirin in stable cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1319–1330. - PubMed
-
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in Type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117–2128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

