Preoperative hyperlactatemia and early mortality after liver transplantation: selection of important variables using random forest survival analysis
- PMID: 35139616
- PMCID: PMC8828623
- DOI: 10.17085/apm.21049
Preoperative hyperlactatemia and early mortality after liver transplantation: selection of important variables using random forest survival analysis
Abstract
Background: Generally, lactate levels > 2 mmol/L represent hyperlactatemia, whereas lactic acidosis is often defined as lactate > 4 mmol/L. Although hyperlactatemia is common finding in liver transplant (LT) candidates, association between lactate and organ failures with Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure (ACLF) is poorly studied. We searched the important variables for pre-LT hyperlactatemia and examined the impact of preoperative hyperlactatemia on early mortality after LT.
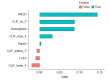
Methods: A total of 2,002 patients from LT registry between January 2008 and February 2019 were analyzed. Six organ failures (liver, kidney, brain, coagulation, circulation, and lung) were defined by criteria of EASL-CLIF ACLF Consortium. Variable importance of preoperative hyperlactatemia was examined by machine learning using random survival forest (RSF). Kaplan-Meier Survival curve analysis was performed to assess 90-day mortality.
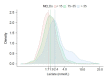
Results: Median lactate level was 1.9 mmol/L (interquartile range: 1.4, 2.4 mmol/L) and 107 (5.3%) patients showed > 4.0 mmol/L. RSF analysis revealed that the four most important variables for hyperlactatemia were MELD score, circulatory failure, hemoglobin, and respiratory failure. The 30-day and 90-day mortality rates were 2.7% and 5.1%, whereas patients with lactate > 4.0 mmol/L showed increased rate of 15.0% and 19.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: About 50% and 5% of LT candidates showed pre-LT hyperlactatemia of > 2.0 mmol/L and > 4.0 mmol/L, respectively. Pre-LT lactate > 4.0 mmol/L was associated with increased early post-LT mortality. Our results suggest that future study of correcting modifiable risk factors may play a role in preventing hyperlactatemia and lowering early mortality after LT.
Keywords: Early mortality; Lactate; Liver transplantation; Random survival.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Cardoso FS, Abraldes JG, Sy E, Ronco JJ, Bagulho L, Mcphail MJ, et al. Lactate and number of organ failures predict intensive care unit mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2019;39:1271–80. - PubMed
-
- Sundaram V, Jalan R, Wu T, Volk ML, Asrani SK, Klein AS, et al. Factors associated with survival of patients with severe acute-on-chronic liver failure before and after liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1381–91.e3. - PubMed
-
- Jeppesen JB, Mortensen C, Bendtsen F, Møller S. Lactate metabolism in chronic liver disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2013;73:293–9. - PubMed
-
- Jalan R, Saliba F, Pavesi M, Amoros A, Moreau R, Ginès P, et al. CANONIC study investigators of the EASL-CLIF Consortium. Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014;61:1038–47. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

