Pelvic inflammatory disease with obstructive complications: two cases and a literature review
- PMID: 35139625
- PMCID: PMC10754370
- DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2022021
Pelvic inflammatory disease with obstructive complications: two cases and a literature review
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
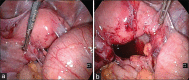
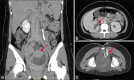
Similar articles
-
[Pelvic actinomycosis: a case with secondary localization in the liver].Presse Med. 1999 Dec 4;28(38):2098-9. Presse Med. 1999. PMID: 10613196 French.
-
Ureteric obstruction caused by pelvic actinomycosis.Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2002 Feb;36(1):87-8. doi: 10.1080/003655902317259454. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12002367
-
Salpingitis and pelvic inflammatory disease.Am Fam Physician. 1985 Jan;31(1):143-9. Am Fam Physician. 1985. PMID: 3966303
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease, laparoscopy, and the expenditure of health care dollars.Int J Fertil. 1987 Jan-Feb;32(1):17-25, 29-32, 36-7. Int J Fertil. 1987. PMID: 2880812 Review. No abstract available.
-
The intrauterine contraceptive device: an often-forgotten and maligned method of contraception.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Jul;181(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70426-6. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10411781 Review.
Cited by
-
Wireless Peristaltic Pump for Transporting Viscous Fluids and Solid Cargos in Confined Spaces.Adv Funct Mater. 2024 Nov 5;34(45):2405865. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202405865. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Adv Funct Mater. 2024. PMID: 39990857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunham RC, Gottlieb SL, Paavonen J. Pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2039–48. - PubMed
-
- Landers DV. Tubo-ovarian abscess complicating pelvic inflammatory disease. In: Landers DV, Sweet RL, editors. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. New York: Springer; 1997. pp. 94–106.
-
- Chappell CA, Wiesenfeld HC. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of severe pelvic inflammatory disease and tuboovarian abscess. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2012;55:893–903. - PubMed
-
- McNeeley SG, Hendrix SL, Mazzoni MM, Kmak DC, Ransom SB. Medically sound, cost-effective treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease and tuboovarian abscess. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;178:1272–8. - PubMed
-
- Sam JW, Jacobs JE, Birnbaum BA. Spectrum of CT findings in acute pyogenic pelvic inflammatory disease. Radiographics. 2002;22:1327–34. - PubMed

