Improving the repair mechanism and miRNA expression profile of tibial defect in rats based on silent information regulator 7 protein analysis of mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 35139764
- PMCID: PMC8973621
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2027066
Improving the repair mechanism and miRNA expression profile of tibial defect in rats based on silent information regulator 7 protein analysis of mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
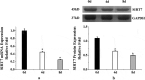
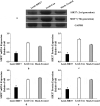
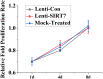
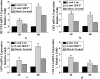
The aim of this study was to verify the role of Silent Information Regulator 7 (SIRT7) in improving the repair mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) and the expression of microribonucleic acid (miRNA). Human BMMSCs were extracted from patients with femoral fractures, and the proliferation activity of human BMMSCs before and after knockout SIRT7 and the expression levels of bone-related genes and proteins were compared. Thirty-two 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into a blank group, a chitosan scaffold group, a control group, and a silence information regulator knockout group 7 (n = 8). In addition to the blank group, the chitosan scaffold, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) transfected stem cell composite chitosan scaffold, and the SIRT7 knockout stem cell composite chitosan scaffold were implanted in the other three groups, respectively. The X-rays and small animal in vivo three-dimensional tomography (Micro-CT) were adopted to quantitatively analyze the volume fraction, the number of trabeculae, and the connection density. Compared with the other three groups, the bone defect was formed more in the medullary mesenchymal stem cell knockout group, and the bone volume fraction, number of trabeculae and connection density were significantly increased (P < 0.05). MiR-98-5p can significantly promote the formation of bone molecules and bone structure in rats (P < 0.05). Human BMMSCs combined with chitosan scaffold can accelerate the repair of tibial defects. MiR-98-5p targeting and regulating bone formation gene (CKIP-1) could significantly improve the process of osteogenesis in rats.
Keywords: BMMSCs; SIRT7 protein; miRNA; tibial defect; tibial defect model.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


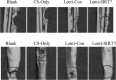
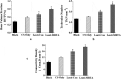
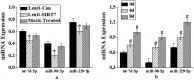

References
-
- Sagi HC, Young ML, Gerstenfeld L, et al. Qualitative and quantitative differences between bone graft obtained from the medullary canal (with a reamer/ irrigator/ aspirator) and the iliac crest of the same patient. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(23):2128–2135. - PubMed
-
- Wubneh A, Tsekoura EK, Ayranci C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1–30. - PubMed
-
- Bartold PM, Gronthos S, Haynes D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and biologic factors ioading to bone formation. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(21):12–32. 4 6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
