Naso-Bronchial Rhinosporidiosis
- PMID: 35140090
- PMCID: PMC8830203
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-247133
Naso-Bronchial Rhinosporidiosis
Abstract
Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic mucocutaneous granulomatous disease caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi, commonly affecting the nose and nasopharynx. Endobronchial involvement is of rare occurrence but can pose challenging problems for diagnosis, surgical excision and anaesthetic management. We report a 40-year-old man with a history of recurrent nasal rhinosporidiosis who presented with unilateral nasal obstruction, cough, shortness of breath and a radiological feature of left lung collapse. Eight years since the last surgery, he presented with a recurrent lesion in the nose with concurrent endobronchial involvement. The patient underwent excision of the nasal and the endobronchial lesion successfully under general anaesthesia without any complication and good symptomatic improvement. The clinical presentation and the management of endobronchial rhinosporidiosis are discussed here. The surgical difficulties faced during the procedure are highlighted.
Keywords: ear; nasal polyps; nose and throat/otolaryngology; respiratory medicine; tropical medicine (infectious disease).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
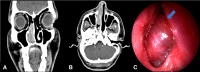
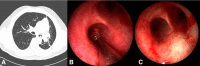
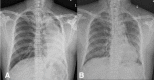

References
-
- BETTS RH, GOPINATH N, THOMAS T. Rhinosporidiosis of the bronchus. Br J Surg 1956;44:316–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
