Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
- PMID: 35140206
- PMCID: PMC8828720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-27980-y
Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
Abstract
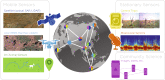
Inexpensive and accessible sensors are accelerating data acquisition in animal ecology. These technologies hold great potential for large-scale ecological understanding, but are limited by current processing approaches which inefficiently distill data into relevant information. We argue that animal ecologists can capitalize on large datasets generated by modern sensors by combining machine learning approaches with domain knowledge. Incorporating machine learning into ecological workflows could improve inputs for ecological models and lead to integrated hybrid modeling tools. This approach will require close interdisciplinary collaboration to ensure the quality of novel approaches and train a new generation of data scientists in ecology and conservation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Committee, T. I. R. L. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species - Strategic Plan 2017-2020. Tech. Rep., IUCN (2017).
-
- Witmer GW. Wildlife population monitoring: some practical considerations. Wild. Res. 2005;32:259–263.
-
- Burghardt GM, et al. Perspectives–minimizing observer bias in behavioral studies: a review and recommendations. Ethology. 2012;118:511–517.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

