Combining p53 mRNA nanotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade reprograms the immune microenvironment for effective cancer therapy
- PMID: 35140208
- PMCID: PMC8828745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28279-8
Combining p53 mRNA nanotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade reprograms the immune microenvironment for effective cancer therapy
Abstract
Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has shown limited benefits in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and other cancers, mediated in part by the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). As p53 loss of function may play a role in immunosuppression, we herein examine the effects of restoring p53 expression on the immune TME and ICB efficacy. We develop and optimize a CXCR4-targeted mRNA nanoparticle platform to effectively induce p53 expression in HCC models. Using p53-null orthotopic and ectopic models of murine HCC, we find that combining CXCR4-targeted p53 mRNA nanoparticles with anti-PD-1 therapy effectively induces global reprogramming of cellular and molecular components of the immune TME. This effect results in improved anti-tumor effects compared to anti-PD-1 therapy or therapeutic p53 expression alone. Thus, our findings demonstrate the reversal of immunosuppression in HCC by a p53 mRNA nanomedicine when combined with ICB and support the implementation of this strategy for cancer treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.G.D. received consultant fees from Bayer, BMS, Simcere, Sophia Biosciences, Innocoll and Surface Oncology and has received research grants from Bayer, Merrimack, Exelixis, Surface Oncology and BMS. No reagents or support from these companies was used for this study. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by other authors.
Figures

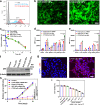
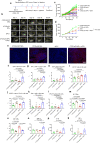
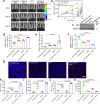
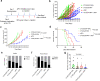
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

