Account of Deep Learning-Based Ultrasonic Image Feature in the Diagnosis of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 35140807
- PMCID: PMC8820903
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8158634
Account of Deep Learning-Based Ultrasonic Image Feature in the Diagnosis of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Acute Kidney Injury
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Account of Deep Learning-Based Ultrasonic Image Feature in the Diagnosis of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Acute Kidney Injury.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9782495. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782495. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946999 Free PMC article.
Abstract
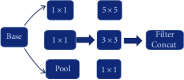
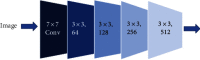
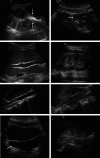
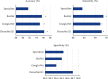
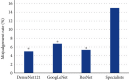
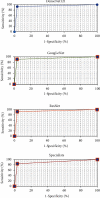
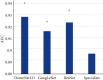
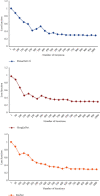
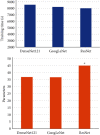
This study was aimed at analyzing the diagnostic value of convolutional neural network models on account of deep learning for severe sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury and providing an effective theoretical reference for the clinical use of ultrasonic image diagnoses. 50 patients with severe sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury and 50 healthy volunteers were selected in this study. They all underwent ultrasound scans. Different deep learning convolutional neural network models dense convolutional network (DenseNet121), Google inception net (GoogLeNet), and Microsoft's residual network (ResNet) were used for training and diagnoses. Then, the diagnostic results were compared with professional image physicians' artificial diagnoses. The results showed that accuracy and sensitivity of the three deep learning algorithms were significantly higher than professional image physicians' artificial diagnoses. Besides, the error rates of the three algorithm models for severe sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury were significantly lower than professional physicians' artificial diagnoses. The areas under curves (AUCs) of the three algorithms were significantly higher than AUCs of doctors' diagnosis results. The loss function parameters of DenseNet121 and GoogLeNet were significantly lower than that of ResNet, with the statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in training time of ResNet, GoogLeNet, and DenseNet121 algorithms under deep learning, as the convergence was reached after 700 times, 700 times, and 650 times, respectively (P > 0.05). In conclusion, the value of the three algorithms on account of deep learning in the diagnoses of severe sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury was higher than professional physicians' artificial judgments and had great clinical value for the diagnoses and treatments of the disease.
Copyright © 2022 Yi Lv and Zhijia Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence Pulse Coupled Neural Network Algorithm in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Acute Kidney Injury under Ultrasound Image.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Jul 20;2021:6761364. doi: 10.1155/2021/6761364. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34336164 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic Image Features under the Intelligent Algorithm in the Diagnosis of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Renal Injury.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 11;2022:2310014. doi: 10.1155/2022/2310014. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9843757. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843757. PMID: 35991127 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Characteristics of Computed Tomography Images for Patients with Acute Liver Injury Caused by Sepsis under Deep Learning Algorithm.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Mar 20;2022:9322196. doi: 10.1155/2022/9322196. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35360262 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Artificial Intelligence for Endoscopic Ultrasound.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2025 Apr;35(2):407-418. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2024.10.007. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2025. PMID: 40021237 Review.
-
Deep Learning for Pulmonary Image Analysis: Classification, Detection, and Segmentation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1213:47-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-33128-3_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32030662 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Account of Deep Learning-Based Ultrasonic Image Feature in the Diagnosis of Severe Sepsis Complicated with Acute Kidney Injury.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9782495. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782495. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946999 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese experts' consensus on the application of intensive care big data.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 8;10:1174429. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1174429. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38264049 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of machine learning-based research in acute kidney injury worldwide.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 17;11:1136939. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1136939. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37006534 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of Transfer Learning Approaches in the Machine Learning of Digital Health Sensing Data.J Pers Med. 2023 Dec 12;13(12):1703. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121703. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023 Feb 20;8(2):129. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8020129. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36828545 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

