Appendiceal disease in hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 35140939
- PMCID: PMC8813669
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.5047
Appendiceal disease in hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
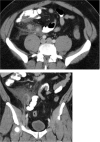
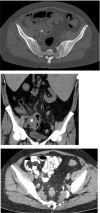
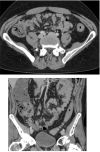
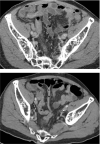
Appendiceal diseases are rare reported complications during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with no guidance on management in the published literature. Medical therapy may be considered in selected patients prior to surgical solutions.
Keywords: appendiceal disease; chemotherapy; hematopoietic stem cell transplant; immunocompromised; medical management.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Koretz MJ, Neifeld JP. Emergency surgical treatment for patients with acute leukemia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985;161:149‐151. - PubMed
-
- Jones AD, Maziarz R, Gilster J, Domreis J, Deveney CW, Sheppard BC. Surgical complications of bone marrow transplantation. Am J Surg. 2003;185(5):481‐484. - PubMed
-
- Hobson MJ, Carney DE, Molik KA, et al. Appendicitis in childhood hematologic malignancies: analysis and comparison with typhlitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:214‐219. - PubMed
-
- Forghieri F, Luppi M, Narni F, et al. Acute appendicitis in adult neutropenic patients with hematologic malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42(10):701‐703. - PubMed
-
- Kontoyiannis DP, Mathur M, Chen Y‐B, Shellito PC, Tse JY. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 13‐2014. A 41‐year‐old man with fever and abdominal pain after stem‐cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(17):1637‐1646. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

