WSSNet: Aortic Wall Shear Stress Estimation Using Deep Learning on 4D Flow MRI
- PMID: 35141290
- PMCID: PMC8818720
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.769927
WSSNet: Aortic Wall Shear Stress Estimation Using Deep Learning on 4D Flow MRI
Abstract
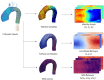
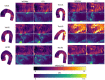
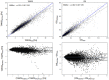
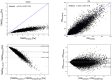
Wall shear stress (WSS) is an important contributor to vessel wall remodeling and atherosclerosis. However, image-based WSS estimation from 4D Flow MRI underestimates true WSS values, and the accuracy is dependent on spatial resolution, which is limited in 4D Flow MRI. To address this, we present a deep learning algorithm (WSSNet) to estimate WSS trained on aortic computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. The 3D CFD velocity and coordinate point clouds were resampled into a 2D template of 48 × 93 points at two inward distances (randomly varied from 0.3 to 2.0 mm) from the vessel surface ("velocity sheets"). The algorithm was trained on 37 patient-specific geometries and velocity sheets. Results from 6 validation and test cases showed high accuracy against CFD WSS (mean absolute error 0.55 ± 0.60 Pa, relative error 4.34 ± 4.14%, 0.92 ± 0.05 Pearson correlation) and noisy synthetic 4D Flow MRI at 2.4 mm resolution (mean absolute error 0.99 ± 0.91 Pa, relative error 7.13 ± 6.27%, and 0.79 ± 0.10 Pearson correlation). Furthermore, the method was applied on in vivo 4D Flow MRI cases, effectively estimating WSS from standard clinical images. Compared with the existing parabolic fitting method, WSSNet estimates showed 2-3 × higher values, closer to CFD, and a Pearson correlation of 0.68 ± 0.12. This approach, considering both geometric and velocity information from the image, is capable of estimating spatiotemporal WSS with varying image resolution, and is more accurate than existing methods while still preserving the correct WSS pattern distribution.
Keywords: 4D Flow MRI; aorta; computational fluid dynamics; deep learning; wall shear stress (WSS).
Copyright © 2022 Ferdian, Dubowitz, Mauger, Wang and Young.
Conflict of interest statement
Working expenses and a partial stipend for EF were provided by Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Rodríguez-Palomares JF, Dux-Santoy L, Guala A, Kale R, Maldonado G, Teixidó-Turà G, et al. . Aortic flow patterns and wall shear stress maps by 4D-flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the assessment of aortic dilatation in bicuspid aortic valve disease. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. (2018) 20:28. 10.1186/s12968-018-0451-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Ooij P, Markl M, Collins JD, Carr JC, Rigsby C, Bonow RO, et al. . Aortic valve stenosis alters expression of regional aortic wall shear stress: new insights from a 4-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging study of 571 subjects. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e005959. 10.1161/JAHA.117.005959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

