MR fingerprinting for semisolid magnetization transfer and chemical exchange saturation transfer quantification
- PMID: 35141967
- PMCID: PMC9808671
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.4710
MR fingerprinting for semisolid magnetization transfer and chemical exchange saturation transfer quantification
Abstract
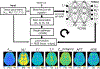
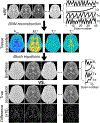
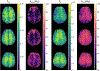
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI has positioned itself as a promising contrast mechanism, capable of providing molecular information at sufficient resolution and amplified sensitivity. However, it has not yet become a routinely employed clinical technique, due to a variety of confounding factors affecting its contrast-weighted image interpretation and the inherently long scan time. CEST MR fingerprinting (MRF) is a novel approach for addressing these challenges, allowing simultaneous quantitation of several proton exchange parameters using rapid acquisition schemes. Recently, a number of deep-learning algorithms have been developed to further boost the performance and speed of CEST and semi-solid macromolecule magnetization transfer (MT) MRF. This review article describes the fundamental theory behind semisolid MT/CEST-MRF and its main applications. It then details supervised and unsupervised learning approaches for MRF image reconstruction and describes artificial intelligence (AI)-based pipelines for protocol optimization. Finally, practical considerations are discussed, and future perspectives are given, accompanied by basic demonstration code and data.
Keywords: CEST; MR fingerprinting (MRF); MT; chemical exchange rate; deep learning; pH; quantitative imaging; unsupervised learning.
© 2022 The Authors. NMR in Biomedicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare the following competing interests: CTF hold a patent for a CEST MR fingerprinting method (patent no. US10,605,877).
Figures


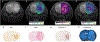
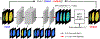

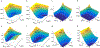
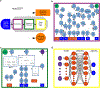
References
-
- Zhou Jinyuan, Payen Jean-Francois, Wilson David A, Traystman Richard J, Van Zijl Peter CM. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat Med. 2003;9:1085–1090. - PubMed
-
- Henkelman R Mark, Huang Xuemei, Xiang Qing-San, Stanisz GJ, Swanson Scott D, Bronskill Michael J. Quantitative interpretation of magnetization transfer. Magn Reson Med. 1993;29:759–766. - PubMed
-
- Balaban Robert S, Ceckler TL. Magnetization transfer contrast in magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic resonance quarterly. 1992;8:116–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

