Hedgehog pathway modulation by glypican 3-conjugated heparan sulfate
- PMID: 35142364
- PMCID: PMC8977055
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.259297
Hedgehog pathway modulation by glypican 3-conjugated heparan sulfate
Abstract
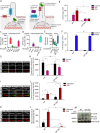
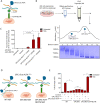
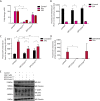
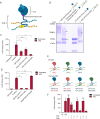
Glypicans are a family of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans that play critical roles in multiple cell signaling pathways. Glypicans consist of a globular core, an unstructured stalk modified with sulfated glycosaminoglycan chains, and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. Though these structural features are conserved, their individual contribution to glypican function remains obscure. Here, we investigate how glypican 3 (GPC3), which is mutated in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel tissue overgrowth syndrome, regulates Hedgehog signaling. We find that GPC3 is necessary for the Hedgehog response, surprisingly controlling a downstream signal transduction step. Purified GPC3 ectodomain rescues signaling when artificially recruited to the surface of GPC3-deficient cells but has dominant-negative activity when unattached. Strikingly, the purified stalk, modified with heparan sulfate but not chondroitin sulfate, is necessary and sufficient for activity. Our results demonstrate a novel function for GPC3-associated heparan sulfate and provide a framework for the functional dissection of glycosaminoglycans by in vivo biochemical complementation. This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
Keywords: Glycosaminoglycans; Glypican; Hedgehog; Heparan sulfate; Signaling.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unraveling Glypican-3: From Structural to Pathophysiological Roles and Mechanisms-An Integrative Perspective.Cells. 2025 May 15;14(10):726. doi: 10.3390/cells14100726. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of glypican-3 in the regulation of body size and cancer.Cell Cycle. 2008 Sep 15;7(18):2787-90. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.18.6672. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18787398
-
The role of glypicans in Hedgehog signaling.Matrix Biol. 2014 Apr;35:248-52. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.007. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24412155 Review.
-
Molecular analysis of a novel intragenic deletion in GPC3 in three cousins with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2017 May;173(5):1400-1405. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38188. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Am J Med Genet A. 2017. PMID: 28371070
-
Glypican-3-deficient mice exhibit developmental overgrowth and some of the abnormalities typical of Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jul 12;146(1):255-64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.255. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10402475 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glycosaminoglycans, Instructive Biomolecules That Regulate Cellular Activity and Synaptic Neuronal Control of Specific Tissue Functional Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2554. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062554. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and Functional Impact of Posttranslational Modification of Glypican-3 on Liver Carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;83(12):1933-1940. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3895. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37027004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling Glypican-3: From Structural to Pathophysiological Roles and Mechanisms-An Integrative Perspective.Cells. 2025 May 15;14(10):726. doi: 10.3390/cells14100726. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Glycosaminoglycan Side Chains and Modular Core Proteins of Heparan Sulphate Proteoglycans and the Varied Ways They Provide Tissue Protection by Regulating Physiological Processes and Cellular Behaviour.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14101. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814101. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans as Potential Markers for In Vitro Human Neural Lineage Specification.Cells. 2025 Jul 26;14(15):1158. doi: 10.3390/cells14151158. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801591 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

