Protective effects of the notoginsenoside R1 on acute lung injury by regulating the miR-128-2-5p/Tollip signaling pathway in rats with severe acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 35142579
- PMCID: PMC8841636
- DOI: 10.1177/17534259211068744
Protective effects of the notoginsenoside R1 on acute lung injury by regulating the miR-128-2-5p/Tollip signaling pathway in rats with severe acute pancreatitis
Abstract
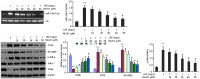
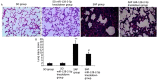
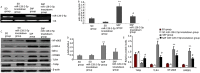
Notoginsenoside R1 (NG-R1), the extract and the main ingredient of Panax notoginseng, has anti-inflammatory effects and can be used in treating acute lung injury (ALI). In this study, we explored the pulmonary protective effect and the underlying mechanism of the NG-R1 on rats with ALI induced by severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). MiR-128-2-5p, ERK1, Tollip, HMGB1, TLR4, IκB, and NF-κB mRNA expression levels were measured using real-time qPCR, and TLR4, Tollip, HMGB1, IRAK1, MyD88, ERK1, NF-κB65, and P-IκB-α protein expression levels using Western blot. The NF-κB and the TLR4 activities were determined using immunohistochemistry, and TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and ICAM-1 levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) using ELISA. Lung histopathological changes were observed in each group. NG-R1 treatment reduced miR-128-2-5p expression in the lung tissue, increased Tollip expression, inhibited HMGB1, TLR4, TRAF6, IRAK1, MyD88, NF-κB65, and p-IκB-α expression levels, suppressed NF-κB65 and the TLR4 expression levels, reduced MPO activity, reduced TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and ICAM-1 levels in BALF, and alleviated SAP-induced ALI. NG-R1 can attenuate SAP-induced ALI. The mechanism of action may be due to a decreased expression of miR-128-2-5p, increased activity of the Tollip signaling pathway, decreased activity of HMGB1/TLR4 and ERK1 signaling pathways, and decreased inflammatory response to SAP-induced ALI. Tollip was the regulatory target of miR-128-2-5p.
Keywords: Notoginsenoside R1; Toll interacting protein; acute lung injury; miR-128-2-5p; pancreatitis; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Pan L, Yu L, Wang Let al. et al. Inflammatory stimuli promote oxidative stress in pancreatic acinar cells via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med 2018; 42: 3582–3590. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Q, Zhang H, Huang Jet al. et al. Melatonin attenuates the inflammatory response via inhibiting the C/EBP homologous protein-mediated pathway in taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis. Int J Mol Med 2018; 42: 3513–3521. - PubMed
-
- Wu XM, Ji KQ, Wang HYet al. et al. microRNA-542–5p protects against acute lung injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis by suppressing the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway through the negative regulation of P21-activated kinase 1. J Cell Biochem 2019; 20: 290–304. - PubMed
-
- Cui HX, Xu JY, Li MQ. Efficacy of continuous renal replacement therapy in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2014; 18: 2523–2526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

