Nevirapine hair and plasma concentrations and HIV-1 viral suppression among HIV infected ante-partum and post-partum women attended in a mother and child prevention program in Maputo city, Mozambique
- PMID: 35143515
- PMCID: PMC8830619
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261522
Nevirapine hair and plasma concentrations and HIV-1 viral suppression among HIV infected ante-partum and post-partum women attended in a mother and child prevention program in Maputo city, Mozambique
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nevirapine hair and plasma concentrations and HIV-1 viral suppression among HIV infected ante-partum and post-partum women attended in a mother and child prevention program in Maputo city, Mozambique.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 26;18(1):e0281190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281190. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36701402 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV (PMTCT) is frequently challenged by irregular access to more effective anti-retroviral therapy. Nevirapine single dose (sdNVP), sdNVP+AZT+3TC for MTCT prophylaxis and NVP+ AZT+3TC for treatment and PMTCT were withdrawn due to low genetic resistance barrier and low efficacy. However current PMTCT lines in Mozambique include DTG+3TC+TDF, TDF+3TC+EFV, DTG +ABC+3TC, and AZT + NVP syrup prophylaxis for exposed babies. We assessed NVP hair and plasma concentrations and association with HIV-1RNA suppression among HIV+ ante-partum and post-partum women under PMTCT in Maputo, Mozambique.
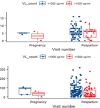
Methods: From December 2013 to November 2014, prospectively were enrolled 200 HIV+ ante-partum women on 200mg nevirapine and zidovudine 300 plus lamivudine 150mg twice daily at least with 3 months treatment and seen again at 24 weeks post-partum. Self-reported pill-taking adherence, NVP concentrations in hair, plasma, hemoglobin, CD4 cell count, HIV-1 RNA load was evaluated. NVP concentration in hair and plasma was analyzed as categorical quartile variable based on better data fit. NVP concentration was set between ≤3.77 ng/ml in plasma and ≤17,20 ng/mg in hair in quartile one to ≥5.36 ng/ml in plasma and ≥53.21 ng/mg in hair in quartile four. Logistic regression models for repeated measures were calculated. Following the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines we set viral suppression at HIV-1RNA < 1000 c/mL. Outcome was HIV-1 RNA<1000 copies/ml. Predictor was NVP concentration in hair categorized in quartiles.
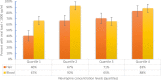
Results: In total 369 person-visits (median of 1.85) were recorded. Self-reported adherence was 98% (IQR 97-100%) at ante-partum. In 25% person visits, NVP concentrations were within therapeutic levels (3.77 ng/ml to 5.35 ng/ml) in plasma and (17.20 ng/mg to 53.20 ng/mg) in hair. In 50% person visits NVP concentrations were above 5.36 ng/ml in plasm and 53.21 ng/mg in hair. HIV-1 RNA suppression was found in 34.7% of women with two viral loads, one at enrollment and another in post-partum. Odds of HIV-1 RNA suppression in quartile 4, was about 6 times higher than in quartile 1 (p-value = 0.006) for NVP hair concentration and 7 times for NVP plasma concentration (p-value = 0.012).
Conclusions: The study results alert for potential low efficacy of current PMTCT drug regimens in use in Mozambique. Affordable means for individual monitoring adherence, ART plasma and hair levels, drug resistant and HIV-1 RNA levels monitoring are recommended for prompt identification of inadequate drug regimens exposure patterns and adjust accordingly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Kusumaningrum A, Ibrahim F, Yunihastuti E, Bela B. HIV Drug Resistance after Failure of 6 Month First-line Therapy in a Hospital: A Case Series. Acta Med Indones. 2019. Jul;51(3):253–2571. - PubMed
-
- WHO Ua U. TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector Progress Report 2010. 2010. Access at https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/2009progressreport/e
-
- Koss CA, Natureeba P, Mwesigwa J, et al.. Hair concentrations of antiretrovirals predict viral suppression in HIV-infected pregnant and breastfeeding Ugandan women [published correction appears in AIDS. 2015 Nov;29(17):2369]. AIDS. 2015;29(7):825–830. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000619 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

