Poor neutralization and rapid decay of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccinated dialysis patients
- PMID: 35143540
- PMCID: PMC8830698
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263328
Poor neutralization and rapid decay of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccinated dialysis patients
Abstract
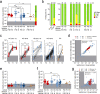
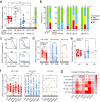
Patients on dialysis are at risk of severe course of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Understanding the neutralizing activity and coverage of SARS-CoV-2 variants of vaccine-elicited antibodies is required to guide prophylactic and therapeutic COVID-19 interventions in this frail population. By analyzing plasma samples from 130 hemodialysis and 13 peritoneal dialysis patients after two doses of BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccines, we found that 35% of the patients had low-level or undetectable IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S). Neutralizing antibodies against the vaccine-matched SARS-CoV-2 and Delta variant were low or undetectable in 49% and 77% of patients, respectively, and were further reduced against other emerging variants. The fraction of non-responding patients was higher in SARS-CoV-2-naïve hemodialysis patients immunized with BNT162b2 (66%) than those immunized with mRNA-1273 (23%). The reduced neutralizing activity correlated with low antibody avidity. Patients followed up to 7 months after vaccination showed a rapid decay of the antibody response with an average 21- and 10-fold reduction of neutralizing antibodies to vaccine-matched SARS-CoV-2 and Delta variant, which increased the fraction of non-responders to 84% and 90%, respectively. These data indicate that dialysis patients should be prioritized for additional vaccination boosts. Nevertheless, their antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 must be continuously monitored to adopt the best prophylactic and therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: J.B., C.S.-F., F.M., C.S., M.Me., E.A.D.J., N.C., E.C., D.C. A.L., and L.Pi. are employees of Vir Biotechnology Inc. and may hold shares in Vir Biotechnology Inc. R.K.G. has received consulting fees from Johnson and Johnson and GlaxoSmithKline for educational activities. The other authors declare no competing interests. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- Anand S, Montez-Rath M, Han J, Bozeman J, Kerschmann R, Beyer P, et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in a large nationwide sample of patients on dialysis in the USA: a cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2020;396(10259):1335–44. Epub 20200925. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32009-2 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7518804. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

