B cell receptor repertoire kinetics after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
- PMID: 35143756
- PMCID: PMC8801326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110393
B cell receptor repertoire kinetics after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
Abstract
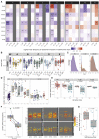
B cells are important in immunity to both severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and vaccination, but B cell receptor (BCR) repertoire development in these contexts has not been compared. We analyze serial samples from 171 SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals and 63 vaccine recipients and find the global BCR repertoire differs between them. Following infection, immunoglobulin (Ig)G1/3 and IgA1 BCRs increase, somatic hypermutation (SHM) decreases, and, in severe disease, IgM and IgA clones are expanded. In contrast, after vaccination, the proportion of IgD/M BCRs increase, SHM is unchanged, and expansion of IgG clones is prominent. VH1-24, which targets the N-terminal domain (NTD) and contributes to neutralization, is expanded post infection except in the most severe disease. Infection generates a broad distribution of SARS-CoV-2-specific clones predicted to target the spike protein, while a more focused response after vaccination mainly targets the spike's receptor-binding domain. Thus, the nature of SARS-CoV-2 exposure differentially affects BCR repertoire development, potentially informing vaccine strategies.
Keywords: B cell receptor repertoire; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bricker T.L., Darling T.L., Hassan A.O., Harastani H.H., Soung A., Jiang X., Dai Y.N., Zhao H., Adams L.J., Holtzman M.J., et al. A single intranasal or intramuscular immunization with chimpanzee adenovirus-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine protects against pneumonia in hamsters. bioRxiv. 2021 36. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

