Seroresponse to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines among Maintenance Dialysis Patients over 6 Months
- PMID: 35144972
- PMCID: PMC8975038
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12250921
Seroresponse to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines among Maintenance Dialysis Patients over 6 Months
Abstract
Background and objectives: Although most patients receiving maintenance dialysis exhibit initial seroresponse to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination, concerns exist regarding the durability of this antibody response. This study evaluated seroresponse over time.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This retrospective cohort study included patients on maintenance dialysis, from a midsize national dialysis provider, who received a complete SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series and had at least one antibody titer checked after full vaccination. IgG spike antibodies (anti-spike IgG) titers were assessed monthly with routine laboratory tests after vaccination; the semiquantitative assay reported a range between zero and ≥20 Index. Descriptive analyses compared trends over time by history of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and vaccine type. Time-to-event analyses examined the outcome of loss of seroresponse (anti-spike IgG <1 Index or development of COVID-19). Cox regression adjusted for additional clinical characteristics.
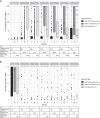
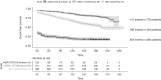
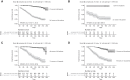
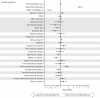
Results: Among 1870 patients receiving maintenance dialysis, 1569 had no prior COVID-19. Patients without prior COVID-19 had declining titers over time. Among 443 recipients of BNT162b2 (Pfizer), median (interquartile range) anti-spike IgG titer declined from ≥20 (5.89 to ≥20) in month 1 after full vaccination to 1.96 (0.60-5.88) by month 6. Among 778 recipients of mRNA-1273 (Moderna), anti-spike IgG titer declined from ≥20 (interquartile range, ≥20 to ≥20) in month 1 to 7.99 (2.61 to ≥20) by month 6. The 348 recipients of Ad26.COV2.S (Janssen) had a lower titer response than recipients of an mRNA vaccine over all time periods. In time-to-event analyses, recipients of Ad26.COV2.S and mRNA-1273 had the shortest and longest time to loss of seroresponse, respectively. The maximum titer reached in the first 2 months after full vaccination was associated with durability of the anti-spike IgG seroresponse; patients with anti-spike IgG titer 1-19.99 had a shorter time to loss of seroresponse compared with patients with anti-spike IgG titer ≥20 (hazard ratio, 15.5; 95% confidence interval, 11.7 to 20.7).
Conclusions: Among patients receiving maintenance dialysis, vaccine-induced seroresponse wanes over time across vaccine types. Early titers after full vaccination are associated with the durability of seroresponse.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccines; SARS-CoV-2; chronic hemodialysis; end-stage renal disease; maintenance; peritoneal dialysis.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
- 335–337
Similar articles
-
BNT162b2 versus mRNA-1273 Third Dose COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients with CKD and Maintenance Dialysis Patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Jan 1;19(1):85-97. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000328. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37847518 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and evolution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein titers after three doses of COVID-19 vaccination in people with HIV.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2024 Aug;57(4):554-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2024.02.004. Epub 2024 Feb 26. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38429206
-
Altered transcriptomic immune responses of maintenance hemodialysis patients to the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine.Elife. 2024 Apr 24;13:e83641. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83641. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38656290 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-analysis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Anti-spike Immunoglobulin G Antibody Durability up to 9 Months After Full Vaccination in Adults.Clin Lab Med. 2025 Mar;45(1):111-136. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2024.10.007. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Clin Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39892931 Review.
-
"COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein-related delayed inflammatory reaction to hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: a challenging clinical conundrum in diagnosis and treatment".Arch Dermatol Res. 2022 Jan;314(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00403-021-02190-6. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022. PMID: 33559733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody titers 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination among patients undergoing hemodialysis in Japan.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022 Oct;26(10):988-996. doi: 10.1007/s10157-022-02243-8. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35751753 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Spike antibodies 3 months after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine booster dose in patients on hemodialysis: the prospective SENCOVAC study.Clin Kidney J. 2022 Jul 26;15(10):1856-1864. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac169. eCollection 2022 Oct. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 36147708 Free PMC article.
-
Growing Understanding of the Clinical and Serologic Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Mar;17(3):335-337. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00320122. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35144971 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Durable Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response after mRNA-1273 Booster in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients during the Omicron Wave.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;11(6):1121. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11061121. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376510 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis post-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccination: A prospective observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 29;102(39):e35484. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035484. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37773791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization : WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard, 2021. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed September 6, 2021
-
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, Perez JL, Pérez Marc G, Moreira ED, Zerbini C, Bailey R, Swanson KA, Roychoudhury S, Koury K, Li P, Kalina WV, Cooper D, Frenck RW Jr, Hammitt LL, Türeci Ö, Nell H, Schaefer A, Ünal S, Tresnan DB, Mather S, Dormitzer PR, Şahin U, Jansen KU, Gruber WC; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group : Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med 383: 2603–2615, 2020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, Diemert D, Spector SA, Rouphael N, Creech CB, McGettigan J, Khetan S, Segall N, Solis J, Brosz A, Fierro C, Schwartz H, Neuzil K, Corey L, Gilbert P, Janes H, Follmann D, Marovich M, Mascola J, Polakowski L, Ledgerwood J, Graham BS, Bennett H, Pajon R, Knightly C, Leav B, Deng W, Zhou H, Han S, Ivarsson M, Miller J, Zaks T; COVE Study Group : Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med 384: 403–416, 2021 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, Cárdenas V, Shukarev G, Grinsztejn B, Goepfert PA, Truyers C, Fennema H, Spiessens B, Offergeld K, Scheper G, Taylor KL, Robb ML, Treanor J, Barouch DH, Stoddard J, Ryser MF, Marovich MA, Neuzil KM, Corey L, Cauwenberghs N, Tanner T, Hardt K, Ruiz-Guiñazú J, Le Gars M, Schuitemaker H, Van Hoof J, Struyf F, Douoguih M; ENSEMBLE Study Group : Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against Covid-19. N Engl J Med 384: 2187–2201, 2021 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brosh-Nissimov T, Orenbuch-Harroch E, Chowers M, Elbaz M, Nesher L, Stein M, Maor Y, Cohen R, Hussein K, Weinberger M, Zimhony O, Chazan B, Najjar R, Zayyad H, Rahav G, Wiener-Well Y: BNT162b2 vaccine breakthrough: Clinical characteristics of 152 fully vaccinated hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Israel. Clin Microbiol Infect 27: 1652–1657, 2021 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

