Diffuse optical reconstructions of functional near infrared spectroscopy data using maximum entropy on the mean
- PMID: 35145148
- PMCID: PMC8831678
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06082-1
Diffuse optical reconstructions of functional near infrared spectroscopy data using maximum entropy on the mean
Abstract
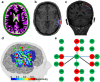
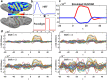
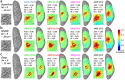
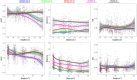
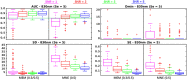
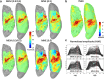
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) measures the hemoglobin concentration changes associated with neuronal activity. Diffuse optical tomography (DOT) consists of reconstructing the optical density changes measured from scalp channels to the oxy-/deoxy-hemoglobin concentration changes within the cortical regions. In the present study, we adapted a nonlinear source localization method developed and validated in the context of Electro- and Magneto-Encephalography (EEG/MEG): the Maximum Entropy on the Mean (MEM), to solve the inverse problem of DOT reconstruction. We first introduced depth weighting strategy within the MEM framework for DOT reconstruction to avoid biasing the reconstruction results of DOT towards superficial regions. We also proposed a new initialization of the MEM model improving the temporal accuracy of the original MEM framework. To evaluate MEM performance and compare with widely used depth weighted Minimum Norm Estimate (MNE) inverse solution, we applied a realistic simulation scheme which contained 4000 simulations generated by 250 different seeds at different locations and 4 spatial extents ranging from 3 to 40[Formula: see text] along the cortical surface. Our results showed that overall MEM provided more accurate DOT reconstructions than MNE. Moreover, we found that MEM was remained particularly robust in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. The proposed method was further illustrated by comparing to functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) activation maps, on real data involving finger tapping tasks with two different montages. The results showed that MEM provided more accurate HbO and HbR reconstructions in spatial agreement with the main fMRI cluster, when compared to MNE.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a personalized functional near infra-red optical tomography workflow using maximum entropy on the mean.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Oct 15;42(15):4823-4843. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25566. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 34342073 Free PMC article.
-
EEG/MEG source imaging of deep brain activity within the maximum entropy on the mean framework: Simulations and validation in epilepsy.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Jul 15;45(10):e26720. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26720. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38994740 Free PMC article.
-
MEG-EEG Information Fusion and Electromagnetic Source Imaging: From Theory to Clinical Application in Epilepsy.Brain Topogr. 2015 Nov;28(6):785-812. doi: 10.1007/s10548-015-0437-3. Epub 2015 May 28. Brain Topogr. 2015. PMID: 26016950 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of weighted minimum-norm estimation with Tikhonov regularization for neuromagnetic source imaging].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Mar;20(1):157-61. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 12744189 Review. Chinese.
-
Development of volume conductor and source models to localize epileptic foci.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 Apr;24(2):101-19. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e318038fb3e. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17414966 Review.
Cited by
-
Tutorial on methods for estimation of optical absorption and scattering properties of tissue.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Jun;29(6):060801. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.6.060801. Epub 2024 Jun 11. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 38864093 Free PMC article.
-
Consistency of electrical source imaging in presurgical evaluation of epilepsy across different vigilance states.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Feb;11(2):389-403. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51959. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38217279 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical Bayesian modeling of the relationship between task-related hemodynamic responses and cortical excitability.Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 Feb 15;44(3):876-900. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26107. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 36250709 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a personalized functional near infra-red optical tomography workflow using maximum entropy on the mean.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Oct 15;42(15):4823-4843. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25566. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 34342073 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and advances in optical 3D mesoscale imaging.J Microsc. 2022 Jun;286(3):201-219. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13109. Epub 2022 May 5. J Microsc. 2022. PMID: 35460574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boas DA, et al. Imaging the body with diffuse optical tomography. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2001;18:57–75. doi: 10.1109/79.962278. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

