Molecular origin of somatostatin-positive neuron vulnerability
- PMID: 35145229
- PMCID: PMC9133093
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-022-01463-4
Molecular origin of somatostatin-positive neuron vulnerability
Abstract
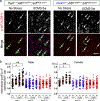
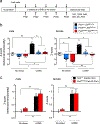
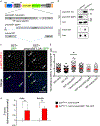
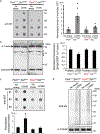
Reduced somatostatin (SST) and dysfunction of SST-positive (SST+) neurons are hallmarks of neurological disorders and associated with mood disturbances, but the molecular origin of SST+ neuron vulnerability is unknown. Using chronic psychosocial stress as a paradigm to induce elevated behavioral emotionality in rodents, we report a selective vulnerability of SST+ neurons through exacerbated unfolded protein response (UPR) of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), or ER stress, in the prefrontal cortex. We next show that genetically suppressing ER stress in SST+ neurons, but not in pyramidal neurons, normalized behavioral emotionality induced by psychosocial stress. In search for intrinsic factors mediating SST+ neuron vulnerability, we found that the forced expression of the SST precursor protein (preproSST) in SST+ neurons, mimicking psychosocial stress-induced early proteomic changes, induces ER stress, whereas mature SST or processing-incompetent preproSST does not. Biochemical analyses further show that psychosocial stress induces SST protein aggregation under elevated ER stress conditions. These results demonstrate that SST processing in the ER is a SST+ neuron-intrinsic vulnerability factor under conditions of sustained or over-activated UPR, hence negatively impacting SST+ neuron functions. Combined with observations in major medical illness, such as diabetes, where excess ER processing of preproinsulin similarly causes ER stress and β cell dysfunction, this suggests a universal mechanism for proteinopathy that is induced by excess processing of native endogenous proteins, playing critical pathophysiological roles that extend to neuropsychiatric disorders.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Epelbaum J, Guillou J-L, Gastambide F, Hoyer D, Duron E, Viollet C. Somatostatin, Alzheimer’s disease and cognition: an old story coming of age? Prog Neurobiol 2009; 89(2): 153–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

