Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases
- PMID: 35145250
- PMCID: PMC9059418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41574-021-00626-7
Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases
Abstract
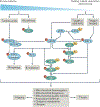
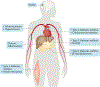
Organismal ageing is accompanied by progressive loss of cellular function and systemic deterioration of multiple tissues, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death. Mitochondria have become recognized not merely as being energy suppliers but also as having an essential role in the development of diseases associated with ageing, such as neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases. A growing body of evidence suggests that ageing and age-related diseases are tightly related to an energy supply and demand imbalance, which might be alleviated by a variety of interventions, including physical activity and calorie restriction, as well as naturally occurring molecules targeting conserved longevity pathways. Here, we review key historical advances and progress from the past few years in our understanding of the role of mitochondria in ageing and age-related metabolic diseases. We also highlight emerging scientific innovations using mitochondria-targeted therapeutic approaches.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
D.A.S. is a founder, equity owner, advisor to, director of, board member of, consultant to, investor in and/or inventor on patents licensed to Revere Biosensors, UpRNA, GlaxoSmithKline, Wellomics, DaVinci Logic, InsideTracker (Segterra), Caudalie, Animal Biosciences, Longwood Fund, Catalio Capital Management, Frontier Acquisition Corporation, AFAR (American Federation for Aging Research), Life Extension Advocacy Foundation (LEAF), Cohbar, Galilei, EMD Millipore, Zymo Research, Immetas, Bayer Crop Science, EdenRoc Sciences (and affiliates Arc-Bio, Dovetail Genomics, Claret Bioscience, MetroBiotech, Astrea, Liberty Biosecurity and Delavie), Life Biosciences, Alterity, ATAI Life Sciences, Levels Health, Tally (aka Longevity Sciences) and Bold Capital. D.A.S. is an inventor on a patent application filed by Mayo Clinic and Harvard Medical School that has been licensed to Elysium Health. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Poulain M, Herm A & Pes G The Blue Zones: areas of exceptional longevity around the world. Vienna Yearb. Popul. Res 11, 87–108 (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

