A genetically encoded sensor for in vivo imaging of orexin neuropeptides
- PMID: 35145320
- PMCID: PMC8831244
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01390-2
A genetically encoded sensor for in vivo imaging of orexin neuropeptides
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A genetically encoded sensor for in vivo imaging of orexin neuropeptides.Nat Methods. 2022 Apr;19(4):505. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01449-8. Nat Methods. 2022. PMID: 35354982 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
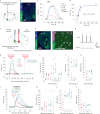
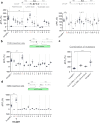
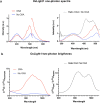
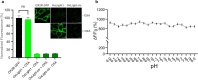
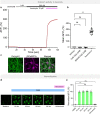
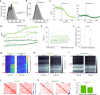
Orexins (also called hypocretins) are hypothalamic neuropeptides that carry out essential functions in the central nervous system; however, little is known about their release and range of action in vivo owing to the limited resolution of current detection technologies. Here we developed a genetically encoded orexin sensor (OxLight1) based on the engineering of circularly permutated green fluorescent protein into the human type-2 orexin receptor. In mice OxLight1 detects optogenetically evoked release of endogenous orexins in vivo with high sensitivity. Photometry recordings of OxLight1 in mice show rapid orexin release associated with spontaneous running behavior, acute stress and sleep-to-wake transitions in different brain areas. Moreover, two-photon imaging of OxLight1 reveals orexin release in layer 2/3 of the mouse somatosensory cortex during emergence from anesthesia. Thus, OxLight1 enables sensitive and direct optical detection of orexin neuropeptides with high spatiotemporal resolution in living animals.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.P. is a co-inventor on a patent application related to the technology described in this article. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Sakurai T, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–585. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Hara J, et al. Genetic ablation of orexin neurons in mice results in narcolepsy, hypophagia, and obesity. Neuron. 2001;30:345–354. - PubMed
-
- Willie JT, et al. Distinct narcolepsy syndromes in orexin receptor-2 and orexin null mice: molecular genetic dissection of non-REM and REM sleep regulatory processes. Neuron. 2003;38:715–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

