Prediction of the Effects of Empagliflozin on Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes Based on Short-Term Changes in Multiple Risk Markers
- PMID: 35145402
- PMCID: PMC8821652
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.786706
Prediction of the Effects of Empagliflozin on Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes Based on Short-Term Changes in Multiple Risk Markers
Abstract
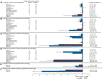
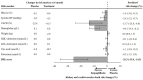
Aims: The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial demonstrated that the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT2) empagliflozin reduces the risk of cardiovascular (CV) and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. We previously developed the parameter response efficacy (PRE) score, which translates drug effects on multiple short-term risk markers into a predicted long-term treatment effect on clinical outcomes. The main objective of this study was to assess the accuracy of the PRE score in predicting the efficacy of empagliflozin in reducing the risk of CV and kidney outcomes. Methods: Short-term (baseline to 6-months) changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), systolic blood pressure (SBP), urinary-albumin-creatinine-ratio (UACR), hemoglobin, body weight, high-density-lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, uric acid, and potassium were determined among 7020 patients with type 2 diabetes and established CV disease in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. The beta-coefficients, derived from a Cox proportional hazards model in a pooled database consisting of 6355 patients with type 2 diabetes, were applied to the short-term risk markers in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial to predict the empagliflozin-induced impact on CV (defined as a composite of non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, or CV death) and kidney (defined as a composite of doubling of serum creatinine or end-stage kidney disease) outcomes. Results: Empagliflozin compared to placebo reduced HbA1c (0.6%), SBP (4.2 mmHg), UACR (13.0%), body weight (2.1 kg), uric acid (20.4 μmol/L), and increased hemoglobin (6.6 g/L), LDL-cholesterol (0.1 mmol/L) and HDL-cholesterol (0.04 mmol/L) (all p<0.01). Integrating these effects in the PRE score resulted in a predicted relative risk reduction (RRR) for the CV outcome of 6.4% (95% CI 1.4-11.7), which was less than the observed 14.7% (95% CI 1.3-26.4%) RRR. For the kidney outcome, the PRE score predicted a RRR of 33.4% (95% CI 26.2-39.8); the observed RRR was 46.9% (95% CI 26.8-61.5). In a subgroup of 2,811 patients with UACR ≥30 mg/g at baseline, the PRE score predicted RRR was 40.8% (95% CI 31.2-49.1) vs. the observed RRR of 40.8% (95% CI 12.4-60.0) for the kidney outcome. Conclusions: Integrating multiple short-term risk marker changes in the PRE score underestimated the effect of empagliflozin on CV and kidney outcomes, suggesting that the currently used risk markers do not fully capture the effect of empagliflozin. In patients with increased albuminuria, the PRE score adequately predicted the effect of empagliflozin on kidney outcomes.
Keywords: cardiovascular outcomes; diabetes; empagliflozin; kidney outcomes; risk markers.
Copyright © 2022 Tye, de Vries, Wanner, Denig and Heerspink.
Conflict of interest statement
CW has received honoraria for consultancy and lecturing from AstraZeneca, Bayer, BI, GlaxoSmithKline, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck Sharp & Dome, Mundipharma, Sanofi Genzyme, and Takeda. HH is a consultant for AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Fresenius, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe and MundiPharma and has a policy that all honoraria are paid to his employer. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prediction of the Effects of Liraglutide on Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes Based on Short-Term Changes in Multiple Risk Markers.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 13;13:786767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.786767. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496307 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of empagliflozin on the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease: an exploratory analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017 Aug;5(8):610-621. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30182-1. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28666775
-
Empagliflozin and Cardio-renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease - Implications for Clinical Practice.Eur Endocrinol. 2018 Sep;14(2):40-49. doi: 10.17925/EE.2018.14.2.40. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Eur Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30349593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Benefit of Empagliflozin Across the Spectrum of Cardiovascular Risk Factor Control in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Sep 1;105(9):3025-35. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa321. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32485734 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Class effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Aug 5;18(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0903-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31382965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repurposing SGLT-2 Inhibitors to Target Aging: Available Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 14;23(20):12325. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012325. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The legacy effect of hyperglycemia and early use of SGLT-2 inhibitors: a cohort study with newly-diagnosed people with type 2 diabetes.Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2023 Jun 12;31:100666. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100666. eCollection 2023 Aug. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2023. PMID: 37547276 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term anti-remodeling effects of gliflozins in diabetic patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: an explainable artificial intelligence approach.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1175606. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175606. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37361206 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the Effects of Liraglutide on Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes Based on Short-Term Changes in Multiple Risk Markers.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 13;13:786767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.786767. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496307 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis and Personalized In Silico Prediction of Treatment Efficacy in Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;16(9):1298. doi: 10.3390/ph16091298. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anker S. D., Butler J., Filippatos G., Khan M. S., Marx N., Lam C. S. P., et al. (2021). Effect of Empagliflozin on Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure by Baseline Diabetes Status: Results from the EMPEROR-Reduced Trial. Circulation 143, 337–349. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051824 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnett A. H., Mithal A., Manassie J., Jones R., Rattunde H., Woerle H. J., et al. (2014). Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin Added to Existing Antidiabetes Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2, 369–384. 10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70208-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

