Tetramethylpyrazine: An Active Ingredient of Chinese Herbal Medicine With Therapeutic Potential in Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Fibrosis
- PMID: 35145414
- PMCID: PMC8821904
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.820071
Tetramethylpyrazine: An Active Ingredient of Chinese Herbal Medicine With Therapeutic Potential in Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Fibrosis
Abstract
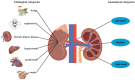
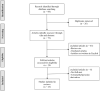
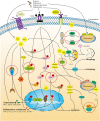
As an increasing public health concern worldwide, acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by rapid deterioration of kidney function. Although continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) could be used to treat severe AKI, effective drug treatment methods for AKI are largely lacking. Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) is an active ingredient of Chinese herb Ligusticum wallichii (Chuan Xiong) with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions. In recent years, more and more clinical and experimental studies suggest that TMP might effectively prevent AKI. The present article reviews the potential mechanisms of TMP against AKI. Through search and review, a total of 23 studies were finally included. Our results indicate that the undergoing mechanisms of TMP preventing AKI are mainly related to reducing oxidative stress injury, inhibiting inflammation, preventing apoptosis of intrinsic renal cells, and regulating autophagy. Meanwhile, given that AKI and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are very tightly linked by each other, and AKI is also an important inducement of CKD, we thus summarized the potential of TMP impeding the progression of CKD through anti-renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Chinese medicine; acute kidney injury; mechanism; renal fibrosis; tetramethylpyrazine.
Copyright © 2022 Li and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tetramethylpyrazine identified by a network pharmacology approach ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative organ injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:638-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.09.034. Epub 2015 Oct 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26435225
-
Baicalin: a potential therapeutic agent for acute kidney injury and renal fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 22;16:1511083. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1511083. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39911847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactoferrin Contributes a Renoprotective Effect in Acute Kidney Injury and Early Renal Fibrosis.Pharmaceutics. 2020 May 8;12(5):434. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050434. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32397266 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-enhanced protective effect of tetramethylpyrazine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e113673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113673. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409029 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Herbal Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Apr 18;10:376. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00376. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31057404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tetramethylpyrazine promotes osteo-angiogenesis during bone fracture repair.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jan 17;20(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05371-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39819480 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Cardioprotective Mechanisms of Ligusticum wallichii in Myocardial Infarction Through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 17;19:281-302. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S481499. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39845152 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating ferroptosis in mice.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2523573. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2523573. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40583332 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Health Through Medicine-Food Homology: A Comprehensive Review of Botanical Micronutrients and Their Mechanisms.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 18;16(20):3530. doi: 10.3390/nu16203530. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global trends and prospects related to macrophage in chronic kidney disease: a bibliometric analysis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2423846. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2423846. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39572163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali B. H., Al-Moundhri M., Eldin M. T., Nemmar A., Al-Siyabi S., Annamalai K. (2008). Amelioration of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats by Tetramethylpyrazine, a Major Constituent of the Chinese Herb Ligusticum Wallichi. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 233 (7), 891–896. 10.3181/0711-RM-315 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

