Altered Circulating MicroRNA Profiles After Endurance Training: A Cohort Study of Ultramarathon Runners
- PMID: 35145424
- PMCID: PMC8824535
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.792931
Altered Circulating MicroRNA Profiles After Endurance Training: A Cohort Study of Ultramarathon Runners
Abstract
Background: Despite the positive effects of endurance training on the cardiovascular (CV) system, excessive exercise induces not only physiological adaptations but also adverse changes in CV system, including the heart. We aimed to evaluate the selected miRNAs expression based on bioinformatic analysis and their changes before and after an ultramarathon run.
Materials and methods: Cardiac tissue-specific targets were identified with the Tissue 2.0 database. Gene-gene interaction data were retrieved from the STRING app for Cytoscape. Twenty-three endurance athletes were recruited to the study. Athletes ran to completion (100 km) or exhaustion (52-91 km, median 74 km). All participants completed pre- and post-run testing. miRNAs expressions were measured both before and after the race.
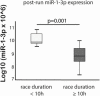
Results: Enrichment analysis of the signaling pathways associated with the genes targeted by miRNAs selected for qRT-PCR validation (miR-1-3p, miR-126, miR-223, miR-125a-5p, miR-106a-5p, and miR-15a/b). All selected miRNAs showed overlap in regulation in pathways associated with cancer, IL-2 signaling, TGF-β signaling as well as BDNF signaling pathway. Analysis of metabolites revealed significant regulation of magnesium and guanosine triphosphate across analyzed miRNA targets. MiR-1-3p, miR-125a-5p, miR-126, and miR-223 expressions were measured in 23 experienced endurance athletes, before and after an ultramarathon wherein athletes ran to completion (100 km) or exhaustion (52-91 km, median 74 km). The expressions of miR-125a-5p, miR-126, and miR-223 were significantly increased after the race (p = 0.007, p = 0.001, p = 0.014, respectively). MiR-1-3p expression post-run showed a negative correlation with the post-run levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) (r = -0.632, p = 0.003). Higher miR-1-3p expression was found in runners, who finished the race under 10 h compared to runners who finished over 10 h (p = 0.001). Post-run miR-125a-5p expression showed a negative correlation with the peak lactate during the run (r = -0.576, p = 0.019).
Conclusion: Extreme physical activity, as exemplified by an ultramarathon, is associated with changes in circulating miRNAs' expression related to inflammation, fibrosis, and cardiac muscle function. In particular, the negative correlations between miR-125a-5p and lactate concentrations, and miR-1-3p and hs-CRP, support their role in specific exercise-induced adaptation. Further studies are essential to validate the long-term effect of these observations.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; endurance sport; in silico prediction; miRNA; microRNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Eyileten, Wicik, Fitas, Marszalek, Simon, De Rosa, Wiecha, Palatini, Postula and Malek.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Circulating microRNAs after a 24-h ultramarathon run in relation to muscle damage markers in elite athletes.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021 Sep;31(9):1782-1795. doi: 10.1111/sms.14000. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021. PMID: 34021921
-
Effects of single bouts of different endurance exercises with different intensities on microRNA biomarkers with and without blood flow restriction: a three-arm, randomized crossover trial.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021 Nov;121(11):3243-3255. doi: 10.1007/s00421-021-04786-2. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34435273 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alterations in Circulating MicroRNAs and the Relation of MicroRNAs to Maximal Oxygen Consumption and Intima-Media Thickness in Ultra-Marathon Runners.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 6;18(14):7234. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147234. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299680 Free PMC article.
-
SIV Infection Regulates Compartmentalization of Circulating Blood Plasma miRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Extracellular Condensates (ECs) and Decreases EV-Associated miRNA-128.Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):622. doi: 10.3390/v15030622. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992331 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review and Bioinformatic Analysis of microRNA Expression in Autism Spectrum Disorder Identifies Pathways Associated With Cancer, Metabolism, Cell Signaling, and Cell Adhesion.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Oct 21;12:630876. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.630876. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34744804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Maximal and sub-maximal exercise tests alter PBMC microRNA expression: insights into sport- and sex-specific variations.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 17;16:1583870. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1583870. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40746988 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of the Diagnostic and Clinical Utility of Salivary microRNAs in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 29;23(21):13160. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113160. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361944 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of circulating platelet-related and diabetes-related microRNAs in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a stepwise hypoglycaemic clamp study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 May 20;21(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01517-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35596173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of structured exercise training on miRNA expression in previously sedentary individuals.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 18;19(12):e0314281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314281. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39693276 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Sports-Related Injuries.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;13(8):1471. doi: 10.3390/genes13081471. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

