Rapid Assessment of Insect Steroid Hormone Entry Into Cultured Cells
- PMID: 35145429
- PMCID: PMC8824665
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.816058
Rapid Assessment of Insect Steroid Hormone Entry Into Cultured Cells
Abstract
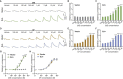
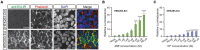
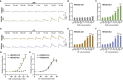
Steroid hormones control development and homeostasis in a wide variety of animals by interacting with intracellular nuclear receptors. Recent discoveries in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster revealed that insect steroid hormones or ecdysteroids are incorporated into cells through a membrane transporter named Ecdysone Importer (EcI), which may become a novel target for manipulating steroid hormone signaling in insects. In this study, we established an assay system that can rapidly assess EcI-mediated ecdysteroid entry into cultured cells. Using NanoLuc Binary Technology (NanoBiT), we first developed an assay to detect ligand-dependent heterodimerization of the ecdysone receptor (EcR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells. We also developed HEK293 cells that stably express EcI. By combining these tools, we can monitor ecdysteroid entry into the cells in real time, making it a reliable system to assess EcI-mediated steroid hormone incorporation into animal cells.
Keywords: Ecdysone Importer; NanoBiT assay; cellular uptake; ecdysone receptor (EcR); ecdysteroid; nuclear receptor (NR); steroid hormone; transporter.
Copyright © 2022 Masterson, Bittar, Chu, Yamanaka and Haga-Yamanaka.
Conflict of interest statement
RB, SH-Y, and NY have a patent (U.S. Patent No. 10,228,380) relevant to this work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transporter-mediated ecdysteroid trafficking across cell membranes: A novel target for insect growth regulators.J Pestic Sci. 2021 Feb 20;46(1):23-28. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.D20-071. J Pestic Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746543 Free PMC article.
-
A Membrane Transporter Is Required for Steroid Hormone Uptake in Drosophila.Dev Cell. 2018 Nov 5;47(3):294-305.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 30293839 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of co-factors for the ligand-mediated activity of the insect ecdysteroid receptor in yeast.J Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Oct;27(2):191-209. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0270191. J Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11564603
-
Hormone receptors and the regulation of insect metamorphosis.Receptor. 1993 Fall;3(3):203-9. Receptor. 1993. PMID: 8167571 Review.
-
Recent progress in understanding the role of ecdysteroids in adult insects: Germline development and circadian clock in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.Zoological Lett. 2015 Nov 2;1:32. doi: 10.1186/s40851-015-0031-2. eCollection 2015. Zoological Lett. 2015. PMID: 26605077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Key Regulatory Genes in Metisa plana Hormone Pathways.Insects. 2023 May 30;14(6):503. doi: 10.3390/insects14060503. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37367319 Free PMC article.
-
Essential functions of mosquito ecdysone importers in development and reproduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 21;119(25):e2202932119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202932119. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35696563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clemons M., Goss P. (2001). Estrogen and the risk of breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 344 276–285. - PubMed
-
- Dhadialla T. S., Retnakaran A., Smagghe G. (2005). “Insect growth- and development-disrupting insecticides,” in Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science, eds Gilbert L. I., Iatrou K., Gill S. S. (Amsterdam: Elsevier; ), 55–115. 10.3390/molecules24234304 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

