Angiopoietin-Like Protein 8/Leptin Crosstalk Influences Cardiac Mass in Youths With Cardiometabolic Risk: The BCAMS Study
- PMID: 35145478
- PMCID: PMC8821093
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.788549
Angiopoietin-Like Protein 8/Leptin Crosstalk Influences Cardiac Mass in Youths With Cardiometabolic Risk: The BCAMS Study
Abstract
Objectives: The link between excess adiposity and left ventricular hypertrophy is multifaceted with sparse data among youths. Given that adipokines/hepatokines may influence lipid metabolism in myocardium, we aimed to investigate the relation of the novel hepatokine angiopoietin-like protein 8 (ANGPTL8) and other adipokines with cardiac structure in a cohort of youths and explore to what extent these adipokines/hepatokines affect cardiac structure through lipids.
Methods: A total of 551 participants (aged 15-28 years) from the Beijing Child and Adolescent Metabolic Syndrome Study (BCAMS) cohort underwent echocardiographic measurements plus a blood draw assayed for five adipokines/hepatokines including adiponectin, leptin, retinol binding protein 4, fibroblast growth protein 21 and ANGPTL8.
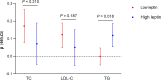
Results: Both ANGPTL8 (β = -0.68 g/m2.7 per z-score, P= 0.015) and leptin (β = -1.04 g/m2.7 per z-score, P= 0.036) were significantly inversely associated with left ventricular mass index (LVMI) independent of classical risk factors. Total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol significantly mediated the ANGPTL8-LVMI association (proportion: 19.0% and 17.1%, respectively), while the mediation effect of triglyceride on the ANGPTL8-LVMI relationship was strongly moderated by leptin levels, significantly accounting for 20% of the total effect among participants with higher leptin levels. Other adipokines/hepatokines showed no significant association with LVMI after adjustment for body mass index.
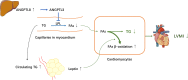
Conclusions: Our findings suggest ANGPTL8, particularly interacting with leptin, might have a protective role in cardiac remodeling among youths with risk for metabolic syndrome. Our results offer insights into the pathogenesis of the cardiomyopathy and the potential importance of tissue-tissue crosstalk in these effects.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03421444.
Keywords: angiopoietin-like protein 8; left ventricular mass; leptin; lipids; youth.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Feng, Wang, Dong, Wang, Zhong, Li, Fu, Xiao, Speakman, Li and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Balagopal PB, de Ferranti SD, Cook S, Daniels SR, Gidding SS, Hayman LL, et al. Nontraditional Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanistic, Research, and Clinical Considerations for Youth: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation (2011) 123(23):2749–69. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31821c7c64 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

