Unexplored parameters of ulnar nerve in the palm and its clinical implications; A cadaveric study
- PMID: 35145657
- PMCID: PMC8818893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103259
Unexplored parameters of ulnar nerve in the palm and its clinical implications; A cadaveric study
Abstract
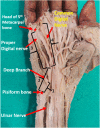
Objectives: Several studies have been conducted on the variations and branching pattern of the ulnar nerve in the hand. There are few studies conducted on defining the distance of ulnar nerve from bony landmarks in the palm. Ulnar nerve is closely related to the pisiform and hook of hamate which act as important landmarks.
Methods: The study was conducted on 30 formalin fixed adult hand specimens in the department of Anatomy. Various measurements related to the ulnar nerve in the palm were taken using a divider and Vernier Calipers and the values were tabulated after obtaining the mean and standard deviation.
Results: The average distance seen in the hand specimens [n = 30] from pisiform to the division of ulnar nerve into superficial and deep branch was 0.89 ± 0.25cm and the distance between pisiform bone up to the division of superficial branch of ulnar nerve into proper and common digital branches was 1.36 ± 0.59 cm. The average distance from the origin of proper digital branch of ulnar nerve to the head of fifth metacarpal bone was 5.25 ± 0.59 cm. The length of common digital branch of ulnar nerve from its origin to division into 2 sensory branches was 4.31 ± 1.09 cm.
Conclusion: This study provides the metric parameters of the ulnar nerve in the hand from its significant bony landmarks which should be kept in mind during surgical procedures to minimize the incidence of injury to its branches. It would assist the orthopedic surgeon in the treatment of ulnar nerve compression in the Guyon's canal.
Keywords: Compression; Guyon's canal; Metacarpal head; Pisiform; Ulnar nerve.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of IJS Publishing Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gray H., Standring S., Ellis H., B Berkovitz B.K. thirty nineth ed. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh, New York: 2005. Gray's Anatomy: the Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice; pp. 932–939. H.
-
- Gross M.S., Gelberman R.H. The anatomy of the distal ulnar tunnel. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1985;196:238–247. - PubMed
-
- Reckelhoff K.E., Jinpu L., Martha A.K., Daniel W.H., Norman W.K. Ultrasound evaluation of the normal ulnar nerve in Guyon's tunnel: cross-sectional area and anthropometric measurements. J. Med. Ultrasound. 2015;23:171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.jmu.2015.09.002. - DOI
-
- Gindha G.S., Kaushal S., Kalyan G.S., Sharma A. Variation in termination of ulnar nerve in hand(trifurcation of ulnar nerve) J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2013;5:326–330.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

