Amelanotic nodular melanoma misdiagnosed as a benign skin lesion: A rare case report from Syria
- PMID: 35145679
- PMCID: PMC8818517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103316
Amelanotic nodular melanoma misdiagnosed as a benign skin lesion: A rare case report from Syria
Abstract
Introduction: and importance: Amelanotic melanoma is a rare and aggressive type of melanoma. It is often diagnosed late because of the lack of melanin in its cells, and this causes treatment delay and, eventually, poor prognosis.
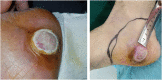
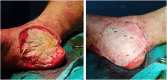
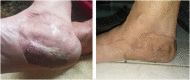
Case presentation: We report a case of a 79-year-old female patient that presented to the dermatology clinic with an asymptomatic lesion on the medial heel of the right foot, with no medical history of previous melanoma or related skin cancer. To get the right diagnosis, an incisional biopsy was performed, and the sample was sent to the pathology laboratory. The sample was stained with S100 and HMB-45 stains, and both were positive. Also, no melanin pigmented cells were seen, so the diagnosis was amelanotic nodular melanoma. The patient was then referred to surgery. The lesion was successfully excised with 5cm safety margins, and the whole lesion was sent to the pathology laboratory to ensure that the edges are malignancy-free. After 18 months of follow-up, the patient is in good health.
Conclusion: Accurate and early diagnosis with appropriate clinical intervention can improve the prognosis and reduce mortality and morbidity rates.
Keywords: Amelanotic; Heel; Melanoma; Nodular; Surgical procedure.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Stojkovic-Filipovic J., Kittler H. Dermatoscopy of amelanotic and hypomelanotic melanoma. J. der Dtsch. Dermatol. Gesellschaft = J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG. 2014 Jun;12(6):467–472. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ani A, Oakley A. Amelanotic melanoma | DermNet NZ [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 Nov 15]. Available from: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/amelanotic-melanoma.
-
- Nalamwar R., Kharkar V., Mahajan S., Chikhalkar S., Khopkar U. Nodular amelanotic melanoma. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2010;76(3):273–275. - PubMed
-
- Gualandri L., Betti R., Crosti C. Clinical features of 36 cases of amelanotic melanomas and considerations about the relationship between histologic subtypes and diagnostic delay. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2009;23(3):283–287. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.03041.x [Internet] Available from: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gibson L.E., Goellner J.R. Amelanotic melanoma: cases studied by Fontana stain, S-100 immunostain, and ultrastructural examination. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1988 Aug;63(8):777–782. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

