Relapse and Outcome of Lupus Nephritis After Renal Transplantation in the Modern Immunosuppressive Era
- PMID: 35145770
- PMCID: PMC8803130
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20863
Relapse and Outcome of Lupus Nephritis After Renal Transplantation in the Modern Immunosuppressive Era
Abstract
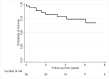
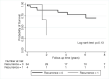
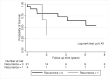
Background Recurrence of lupus nephritis in the graft is a concern in lupus patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing renal transplantation. The recurrence of lupus nephritis has been variable among different studies depending on the patient characteristics, immunosuppressive regimen, and indications of renal biopsy. Therefore, we investigated the recurrence of lupus nephritis among our patients to see if the new post-transplant regimen has impacted the recurrence. Methods We collected data on all recipients with end-stage renal disease secondary to lupus nephritis, who received renal transplants between 2006-2017 in our center. Patient demographics, transplant, and dialysis-related information have been recorded including kidney biopsy, graft loss, and survival were recorded. An association between recurrent lupus nephritis with survival and/or graft loss was examined using survival models. Results The overall mean±SD age at baseline was 42±13 years; 89% were female; 89% were African American; the previous time on dialysis was a median of 4 years (IQR: 2-8 years), 81% received hemodialysis and 31% received living donor transplantation in the cohort. Our patients received the standard immunosuppressive regimen consisting of prednisone, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil. Four (10.5%) of the 38 patients had biopsy-proven lupus nephritis recurrence. A total of 10 patients (26%) had graft loss or died during the median follow-up time of 1,230 days (IQR: 460-2,227 days). Recurrence of lupus nephritis showed a trend for increased risk of graft loss or patient death (Hazard Ratio: 3.14, 95%Confidence Interval: 0.65-15.24) compared to the recipient without recurrence in our unadjusted proportional Cox regression model. Conclusion The recurrence rate of lupus nephritis in our patient population is much lower compared to past studies from different immunosuppressive eras. Patients with recurrent lupus nephritis showed an increased risk of graft loss or death.
Keywords: immunosuppressive; kidney transplantation; lupus nephritis; outcome; relapse; • kidney transplantation • rheumatoid arthritis • anca- associated vasculitis • living kidney donor • esrd.
Copyright © 2022, Pattanaik et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal transplantation in lupus nephritis: a Brazilian cohort.Lupus. 2012 Apr;21(5):570-4. doi: 10.1177/0961203311430220. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Lupus. 2012. PMID: 22129601
-
Outcomes of renal transplantation among patients with end-stage renal disease caused by lupus nephritis.Kidney Int. 2000 May;57(5):2136-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00065.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10792635
-
Kidney transplantation outcomes in lupus nephritis: A 37-year single-center experience from Latin America.Lupus. 2021 Sep;30(10):1644-1659. doi: 10.1177/09612033211028663. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 34225520
-
Outcome of renal transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;27(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(97)80033-9. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1997. PMID: 9287386 Review.
-
Renal transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus and recurrent lupus nephritis. A single-center experience and a review of the literature.Transplantation. 1991 Nov;52(5):805-10. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199111000-00009. Transplantation. 1991. PMID: 1949164 Review.
Cited by
-
Referral and evaluation for kidney transplantation among patients with lupus nephritis-related end-stage kidney disease.Lupus. 2024 Jan;33(1):48-57. doi: 10.1177/09612033231219739. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Lupus. 2024. PMID: 38019182 Free PMC article.
-
The Recurrence of Systemic Diseases in Kidney Transplantation.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 9;14(8):2592. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082592. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Adverse Events Following Immunosuppressant Administration for Pediatric Patients With Renal Transplants Categorized by Two-Year Age Increments Using the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System.Cureus. 2024 Jul 24;16(7):e65300. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65300. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39184624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An assessment of renal failure in an SLE cohort with special reference to ethnicity, over a 25-year period. Adler M, Chambers S, Edwards C, Neild G, Isenberg D. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:1144–1147. - PubMed
-
- Lupus nephritis and kidney transplantation: where are we today? Wong T, Goral S. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019;26:313–322. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
